Remote work isn’t just a trend—it’s the new normal.
According to USA Today, more than half of office workers prefer working from home at least three days a week. The perks? Flexibility, better work-life balance, and no commute. The challenge? Cybersecurity risks.
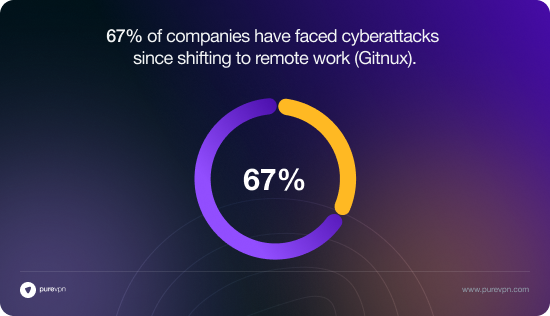
Researchers warn about the rising security threats in remote work.
- 67% of companies have faced cyberattacks since shifting to remote work (Gitnux).
- But there’s hope—94% of those affected say their security improved after adopting cloud solutions.
This article breaks down the biggest cybersecurity risks of remote work in 2025 and how to stay ahead of the threats.
Why Does Remote Work Increase Cybersecurity Risks?
The HP Wolf Security Blurred Lines & Blindspots Report 2021 highlights some key concerns:
- 70% of remote workers use work devices for personal activities.
- Cyberattacks surged by 238% during the pandemic.
- 54% of IT managers saw a rise in phishing attacks, and 56% reported more browser infections.
The takeaway? Remote work brings new threats that office environments don’t face.
Top 6 Cybersecurity Risks in Remote Work
1. Endpoint Vulnerabilities
In offices, IT teams control security. At home, employees rely on personal devices and networks. Cybercriminals exploit these weaker protections with malware and ransomware attacks.
2. Unsecured Wi-Fi Networks
Home and public Wi-Fi are often unsecured, making it easy for hackers to steal passwords and financial data. Some hackers set up fake Wi-Fi networks (“evil twins”) to trick users into connecting and exposing their data. CISA issued a warning last year, urging remote workers to be extra cautious.
3. Insider Threats & Data Theft
Less supervision means some employees cut corners on security. Some may accidentally or intentionally expose sensitive data. Using personal devices on unsecured networks makes it even easier to leak confidential information.
4. Inadequate Access Controls
Employees often have more permissions than they actually need. Security is harder to manage across multiple locations and devices. Hackers exploit weak access controls to gain unauthorized access and steal data.
5. Slow Incident Response Time
Communication delays in remote teams slow down security responses. IBM reports that companies with remote workers take 58 extra days to resolve security breaches. The longer it takes, the more damage a cyberattack can cause.
6. Expanded Attack Surface
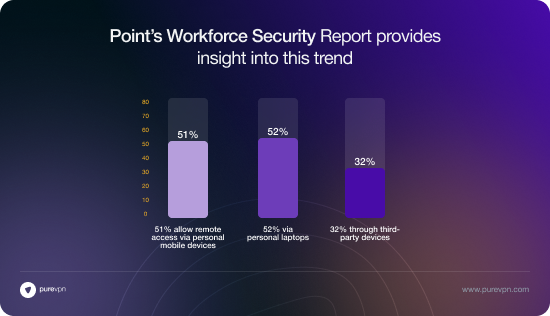
Many companies allow employees to use personal devices for work. Check Point’s Workforce Security Report found:
- 51% of businesses allow access from personal mobile devices.
- 52% permit personal laptops.
- 32% even allow third-party devices.
More devices = more security gaps = higher risk of breaches.
How to Strengthen Remote Work Security
Securing remote teams isn’t just about installing software—it’s about taking proactive steps. Here’s how to reduce vulnerabilities and protect your business:
1. Use Endpoint Protection Solutions
Secure laptops, mobile devices, and home computers with the latest cybersecurity software. Prevent malware infections and stop unauthorized access before it starts.
2. Encrypt Data in Transit & at Rest
Protect sensitive data even if it’s intercepted. Encryption prevents hackers from reading or using stolen data.
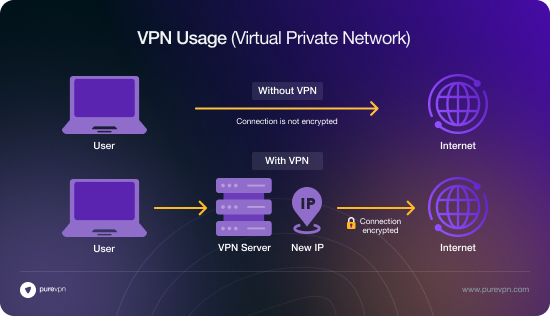
3. Use a Business VPN
A VPN encrypts all internet traffic, securing data on public or home Wi-Fi. It prevents eavesdropping and unauthorized access to company resources. Employees working remotely? A VPN is a must-have.
4. Prioritize Cybersecurity Training
- 30% of remote workers lack security training.
- 44% have never received cybersecurity guidance for remote work (Data Basix).
Regular training = fewer security mistakes and stronger defenses.
How PureVPN for Teams Keeps Remote Work Secure
Encrypted Connections: Protects data from hackers by securing internet traffic.
Dedicated IPs: Provides a fixed, private IP for secure and reliable access.
Centralized Access Control: Lets IT teams manage who can access company resources.
Secure VPN Tunnel: Allows remote teams to work safely from anywhere without data leaks.
Identity-Based Authentication & SSO: Ensures only authorized users can log in.
Role-Based Permissions: Gives employees access only to what they need, reducing risks.
Advanced Security Protocols (WireGuard): Provides fast and secure connections.
Centralized Dashboard: Helps IT teams monitor and control security in one place.
Seamless Collaboration: Keeps teams connected securely without disruptions.

Final Verdict
Remote work is here to stay. But so are its cybersecurity challenges.
- Companies must recognize these risks and take action.
- Adopting best practices and using security solutions like PureVPN for Teams helps tackle threats head-on.
- A secure remote workforce ensures a resilient business.
It’s time to level up your remote security strategy—before it’s too late.