- Data Residency Priority: SaaS data residency requires controlling where customer data is stored and processed to meet regulatory and business requirements.
- Regulatory Compliance: Global regulations like GDPR and country-specific localization laws make compliance essential to avoid fines and reputational risk.
- VPN Routing Benefits: VPN routing helps enforce data residency by geo-restricting traffic, applying access policies, logging activity, and maintaining encryption.
- Challenges: Latency, trust in VPN nodes, policy complexity, and regulator acceptance require careful planning.
- Solution: PureVPN White Label VPN enables SaaS providers to route data securely, maintain audit trails, and comply with residency, sovereignty, and GDPR requirements.
For SaaS providers operating globally, controlling where customer data is stored and processed has become a critical regulatory and business requirement. Governments are increasingly enforcing rules on data residency, auditors demand proof of compliance, and customers expect their data to remain within approved regions.
This makes SaaS data residency a strategic priority, rather than a simple compliance task.
Non-compliance can result in substantial fines, reputational damage, or even loss of access to key markets. Ensuring proper data residency allows SaaS companies to maintain trust, meet legal obligations, and protect sensitive information across borders.
What Is SaaS Data Residency And Why It’s Not Trivial
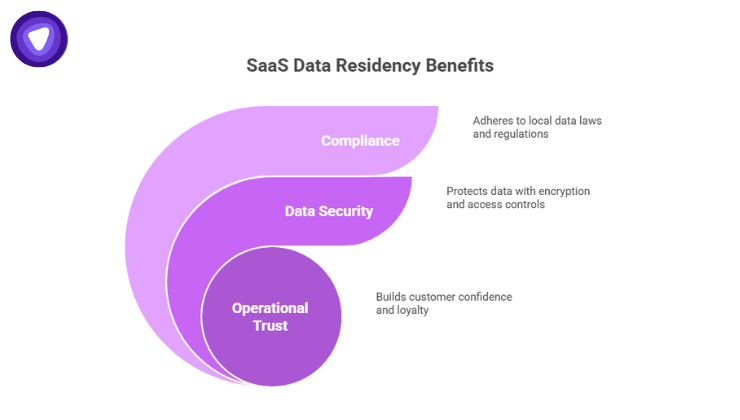
Data residency means controlling the geographic location where data is stored, processed, and managed. For a SaaS company, that often involves designing infrastructure so that customer data from a particular region stays within specific national or regional boundaries.
But it is not just about geography. Proper SaaS data residency addresses:
- Compliance: Meeting local laws that regulate where data must live.
- Data security: Ensuring strong controls, encryption, and access management.
- Operational trust: Demonstrating to customers that their data is handled according to their expectations and legal requirements.
Organizations that ignore these concerns risk significant penalties. According to IBM, in 2023 the EU fined Meta around €1.2 billion for non‑GDPR‑compliant data transfers.
Key Regulatory Drivers: Why Global SaaS Needs Data Residency
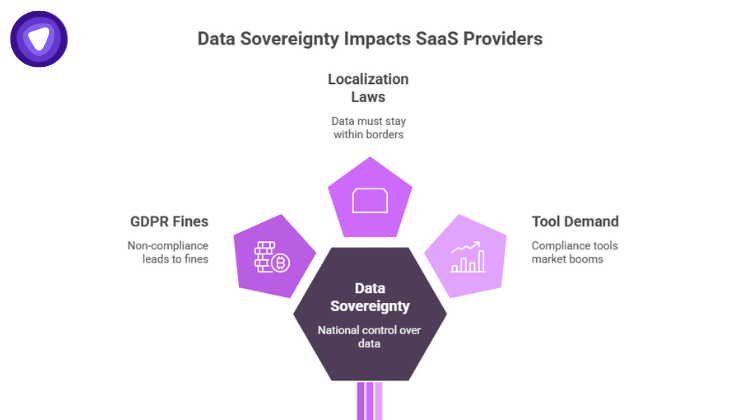
Global SaaS providers must navigate an evolving regulatory landscape where both regional laws and international agreements dictate how data can be stored and transferred.
GDPR and Cross‑Border Transfers
Under the GDPR, transfers of personal data to non-EU countries require that the destination ensures an “adequate” level of protection. Without that, SaaS providers risk steep fines, up to 4% of global annual revenue.
Localization Laws & Data Sovereignty
Many countries now have data residency requirements by country, or even strict data localization laws that force data to remain entirely within national borders. These rules stem from data sovereignty policies, where a nation asserts legal control over data within its territory.
Increasing Demand for Tools & Controls
As regulatory pressure mounts, the market for data residency compliance tools is booming. For example, the data residency and sovereignty compliance tools market is projected to hit USD 228.37 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of nearly 26%. Meanwhile, “Data Residency as a Service” solutions reached USD 2.58 billion in 2024 and are forecasted to grow strongly.
Data Sovereignty vs Data Residency vs Data Localization: What’s the Difference?
These terms are related but distinct, and mixing them up can lead to flawed strategies.
| Term | Meaning | Why It Matters for SaaS |
| Data Sovereignty | Legal concept: a state’s authority over data within its borders. | Determines which laws apply to data. If data resides in your servers, the host country’s regulations might apply. |
| Data Residency | Physical location of data storage and processing. | SaaS must architect infrastructure to meet residency demands. |
| Data Localization | Requirement that data not leave a jurisdiction. | Hardest to comply with. Often requires local infrastructure or partner data centers. |
Understanding these differences ensures that a SaaS provider makes informed decisions around architecture, risk, and compliance.
Common SaaS Data Residency Requirements by Country
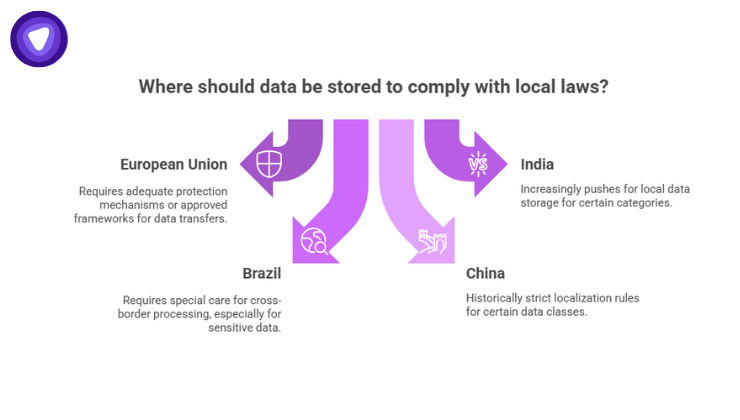
Every country approaches data regulation differently. Some key examples:
- European Union (GDPR): Data transfers require adequate protection mechanisms or approved frameworks (like Standard Contractual Clauses).
- India: Local laws increasingly push for storing certain categories of data within the country.
- Brazil (LGPD): Requires special care for cross-border data processing, especially for sensitive data.
- China: Historically strict localization rules for certain data classes.
Meeting SaaS data residency requirements by country often involves:
- Deploying data centers or cloud regions strategically.
- Classifying data by sensitivity and legal requirement.
- Applying encryption, access controls, and monitoring.
- Maintaining documentation and audit trails for compliance.
How VPN Routing Helps SaaS Achieve Data Residency Compliance

VPN routing is more than security; for SaaS businesses, it is a powerful lever to enforce data residency and sovereignty.
1. Geo‑Restricted Tunneling
By routing traffic through VPN nodes in target jurisdictions, SaaS providers can ensure that data enters and exits networks within compliant regions. This reduces the risk of cross-border leakage.
2. Enforced Access Policies
You can gate data flows via VPN, such that only connections from approved geographic regions reach certain databases or services. This helps meet data localization or residency requirements without replicating entire stacks.
3. Auditability & Logging
A well-architected VPN setup offers detailed logs: which user connected, from where, to which node. These logs become crucial artifacts during compliance audits or regulatory reviews.
4. Segmentation & Encryption
VPNs inherently provide encryption and logical network segmentation. You can isolate sensitive customer data, designating some workloads to route only via sovereign regions.
5. Flexible Scaling
Instead of building full data centers in every country, SaaS companies can deploy fewer regional data stores and leverage VPN routing to meet residency demands, optimizing cost while maintaining compliance.
Challenges & Risks When Using VPN for Data Residency
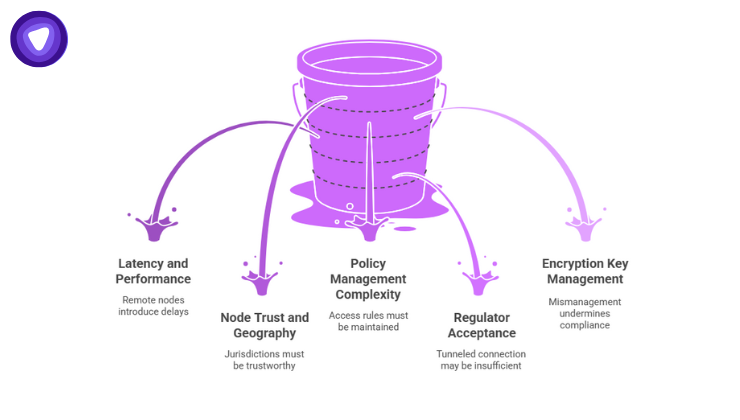
While VPN routing is a powerful tool, be aware of:
- Latency and performance trade‑offs: Routing via remote VPN nodes can introduce delays.
- Node trust and geography: You must have VPN endpoints in jurisdictions that satisfy regulatory needs and that you can trust.
- Complexity of policy management: Access rules, encryption, and logging policies must be carefully designed and maintained.
- Regulator acceptance: Some regulators may not consider a tunneled connection sufficient for data residency; physical storage still matters.
- Encryption key management: If you rely on VPN plus encryption, who holds the keys? Mismanagement can undermine compliance.
Best Practices for SaaS Providers Building Residency-Compliant Infrastructure
To leverage VPN routing effectively for SaaS data residency, follow these guided practices:
- Map Your Regulatory Landscape
- Catalogue countries where your SaaS operates.
- Document local SaaS data residency requirements and data sovereignty laws.
- Understand if localization is required or if flexible residency suffices.
- Catalogue countries where your SaaS operates.
- Classify Your Data
- Identify data objects by sensitivity (PII, telemetry, encrypted logs).
- Use this classification to decide what must be stored regionally and what can be globally accessible.
- Identify data objects by sensitivity (PII, telemetry, encrypted logs).
- Design Network Architecture with Intent
- Deploy regional VPN nodes aligned with your customer footprint.
- Implement segmentation; certain data should only be accessible via particular nodes.
- Deploy regional VPN nodes aligned with your customer footprint.
- Encrypt End-to-End
- Use strong encryption for data both at rest and in transit.
- Manage keys carefully, ideally holding them close to your data stores or in regionally relevant KMS.
- Use strong encryption for data both at rest and in transit.
- Maintain Visibility
- Log all VPN connections and routing decisions.
- Retain logs in compliance‑friendly jurisdictions.
- Generate periodic audit reports for regulatory compliance.
- Log all VPN connections and routing decisions.
- Ensure Legal & Policy Alignment
- Maintain a cross-functional team: legal, compliance, and engineering.
- Regularly review data residency policies against evolving laws.
- Have incident response plans that account for residency violations or routing failures.
- Maintain a cross-functional team: legal, compliance, and engineering.
How PureVPN White Label VPN Solution Supports SaaS in Staying Compliant
PureVPN White Label VPN Solution helps SaaS providers enforce data residency compliance by offering a global network of VPN nodes in key jurisdictions. This enables secure routing of data through approved regions, ensuring that sensitive information stays within required boundaries without the need for multiple physical data centers.
The solution also provides customizable access controls, encrypted tunnels, and detailed logging, allowing SaaS companies to align with SaaS data residency requirements, data sovereignty rules, and GDPR mandates. With PureVPN, providers can confidently manage international data flows while maintaining regulatory compliance and customer trust.
Final Thoughts
SaaS data residency is no longer a niche concern. It sits at the intersection of regulation, trust, and infrastructure. As borders tighten and customers demand more control, SaaS companies must architect for residency, not just by storing data locally but by controlling how it flows.
VPN routing offers a practical, scalable path to compliance, leveraging geographic tunnels, enforcing access, and maintaining visibility. When paired with a solution like PureVPN White Label VPN, it becomes a strategic enabler, reducing compliance risk and building trust with customers around the world.


