- Audit Logs Accountability: Audit logs record who did what, when, and where across systems.
- Exportable Logs: Structured logs from Office 365, Azure, AWS, Linux, and Discord simplify audit preparation.
- SIEM Integration: Dashboards ensure consistent, searchable, and auditor-ready records.
- Standardization & Retention: Standardized formats and retention policies reduce manual effort and support efficient audits.
- Password Management: Combining password management with audit logs strengthens security, traceability, and speeds up external audits.
During an external audit, auditors often ask for a clear record of who accessed which systems and when. Without organized logs, gathering this information can take hours across multiple platforms.
With exportable audit logs in place, from Office 365 to Azure, AWS, Linux, and Discord, you can provide structured, ready-to-review records quickly. Integrating logs with a SIEM system ensures accuracy and consistency, making audit preparation straightforward and efficient.
What Are Audit Logs?
An audit log is a detailed, chronological record of events that tracks who performed an action, what was done, when, where, and often why. Unlike standard system logs, audit logs focus on accountability and traceability.
They record user activity, configuration changes, system access, and other critical events, providing the evidence auditors need to evaluate your security posture.
Key Characteristics of Audit Logs

Properly implemented audit logs provide traceability and accountability, essential for external audit preparation.
- Records significant user and system actions.
- Captures metadata like timestamps, source IPs, and outcomes.
- Supports regulatory, internal, and security audits.
- Can be exported and integrated with SIEM systems for analysis.
Why Audit Logs Matter for External Audits
External auditors require verifiable evidence to validate control over systems and data. Well-maintained audit logs provide:
- Transparency: Clear record of who did what and when.
- Accountability: Shows that unauthorized actions can be detected.
- Forensic readiness: Enables rapid reconstruction of events.
- Efficiency: Exportable logs save hours of manual data collection.
- Deterrence: Knowledge that actions are logged discourages misuse.
A 2024 survey of enterprise logging practices found that organizations with structured, exportable audit logs reduced audit preparation time by up to 60%.
Making Audit Logs Exportable and Audit-Ready
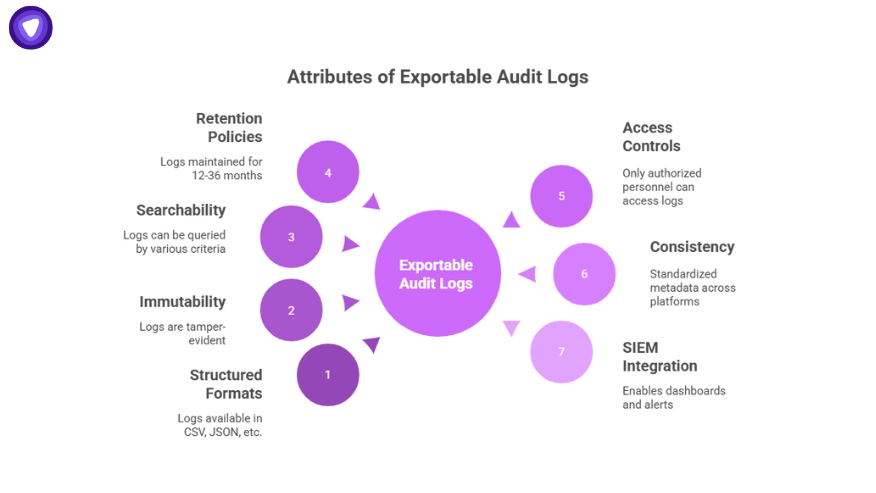
Exportable audit logs are prepared not just for security monitoring but for audit delivery. Key attributes include:
- Structured export formats: CSV, JSON, or other auditor-friendly formats.
- Immutability: Logs should be tamper-evident.
- Searchability: Query by user, resource, or event type.
- Retention policies: Maintain logs for audit periods (12–36 months).
- Access controls: Only authorized personnel can view or export logs.
- Consistency across platforms: Standardized metadata across Office 365, Azure, AWS, and Linux.
- Integration with SIEM: Enables dashboards, alerts, and historical analysis.
With these features, audits become faster, less error-prone, and more reliable.
Audit Logs Across Common Platforms
Here’s a concise table summarizing audit logs across popular platforms:
| Platform | Key Events Tracked | Export/Integration Options | Audit Value |
| Office 365 | User sign-ins, file edits, admin changes | Microsoft Purview, Graph API | Tracks access and configuration changes for auditors |
| Azure | Resource modifications, policy updates | Log Analytics, Event Hub, Storage | Shows cloud resource changes for external audits |
| AWS | API calls, IAM actions, object access | CloudTrail JSON/CSV export | Demonstrates control over cloud infrastructure |
| Linux | File access, system calls, privileged actions | Auditd log export | Provides OS-level evidence for system audits |
| Discord | Admin actions, role changes, moderation | Platform audit log export | Useful for collaboration platform governance |
This table serves as a practical audit logs example, highlighting how structured, exportable logs simplify audit preparation and reduce time spent searching for evidence.
Audit Logs Examples in Detail
Before diving into specific platforms, it’s helpful to understand how audit logs function in practice and the types of events they typically capture.
Audit Logs Office 365
Office 365 logs provide visibility across Exchange, SharePoint, Teams, and Azure AD.
- Actions include mailbox access, file edits, role changes, and administrative operations.
- Export is possible via Microsoft Purview or Graph API.
- Example: An administrator modifies a SharePoint sensitivity label; the audit log records the admin, timestamp, action, and IP address.
These logs are crucial for external auditors verifying access to sensitive data or changes in permissions.
Audit Logs Azure
Azure activity logs monitor resource modifications, policy assignments, and access events.
- Export options include Log Analytics, Event Hub, or storage accounts.
- Provides auditors with cloud resource visibility and proof of change management.
Audit Logs AWS
AWS CloudTrail captures API calls and user/service activity.
- Records events such as StartInstances or S3 object reads.
- Exportable in JSON or CSV formats, making it auditor-ready.
- Example: IAM user “Mateo” starts an EC2 instance; logs include timestamp, action, and source IP.
Audit Logs Linux
Linux audit logs (via auditd) record system-level changes, privileged actions, and file access events.
- Example: /var/log/audit/audit.log logs a user reading /etc/ssh/sshd_config, capturing UID, process ID, and timestamp.
- These logs provide forensic evidence for operating system audits.
Audit Logs Discord
Discord audit logs capture administrative actions, moderation events, and role changes.
- Useful for organizations relying on collaboration tools.
- Export ensures accountability for platform management.
Audit Logs Icon
An audit logs icon in dashboards or portals visually signals the location of logs. This small UI element aids auditors in quickly identifying relevant logs in exported datasets.
How Exportable Audit Logs Accelerate External Audits

Exportable audit logs streamline audits in multiple ways:
- Pre-packaged log sets: Provide filtered datasets ready for auditor review.
- Reduced manual effort: Eliminate manual queries across systems.
- Consistent schema: Easier interpretation for auditors.
- Audit-ready evidence: Formatted, complete, and ready for submission.
- SIEM integration: Dashboards summarize events; raw logs provide detailed evidence.
- Faster investigations: Quickly trace suspicious activities.
- Retention & compliance: Demonstrates controlled, consistent record-keeping.
For instance, when auditors request all role changes in the last six months, pre-exported Office 365 and Azure logs can be delivered immediately, saving days of manual compilation.
Checklist for IT Managers

To ensure audit logs are export-ready:
- Define events to log (admin changes, privilege assignments, file access).
- Enable logging on all key platforms (Office 365, Azure, AWS, Linux).
- Standardize log formats and metadata.
- Set up export mechanisms and verify them.
- Protect log integrity with access controls and tamper-proof storage.
- Implement retention policies aligned with audit cycles.
- Automate log collection and exports.
- Integrate with SIEM for dashboards and alerts.
- Conduct audit drills to validate processes.
- Review logs periodically to ensure completeness and searchability.
Operationalizing Exportable Logs with SIEM
Linking audit logs to a SIEM provides a unified view of security and audit readiness:
- Ingest: Collect logs from all major platforms.
- Normalize: Map diverse schemas to a common structure.
- Alerting & dashboards: Detect anomalies and provide audit evidence.
- Retention & archival: Ensure logs are securely stored and exportable.
- Export capability: Deliver logs in auditor-friendly formats.
- Audit linking: Respond to auditor queries quickly with complete logs.
SIEM integration turns logs into actionable intelligence while simplifying audit preparation.
Common Pitfalls and Solutions
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures a faster, more reliable audit experience.
| Pitfall | Issue | Solution |
| Incomplete logging | Missing key events | Enable logging on all systems by default |
| Unstructured logs | Difficult to export and review | Use standardized, structured formats |
| Tamperable logs | Compromised integrity | Apply immutability and access control |
| Disparate schemas | Manual mapping slows audits | Standardize or transform logs across platforms |
| Short retention | Historical events unavailable | Align retention with audit cycle requirements |
| Manual processes | Time-consuming and error-prone | Automate log collection and exports |
| Overwhelming volume | Hard to find relevant events | Filter, tag, and index events |
| No drill | Surprises during audits | Conduct simulated audit requests |
Bringing It All Together with Password Management
Incorporating a solution like PureVPN White Label Password Manager strengthens audit readiness. Every credential creation, modification, access, and sharing event is logged and exportable, providing structured audit logs aligned with cloud and productivity platforms. It also integrates with SIEM dashboards, offering a complete view of credential access and management.
By combining password management with exportable audit logs, organizations can reduce gaps, ensure all critical actions are traceable, and streamline audit processes. This approach increases accountability and saves significant time during external audits.
Take Control of Your Password Security
Using strong, unique passwords for every account is essential. A password manager makes it effortless to generate, store, and autofill complex passwords—keeping you safe from breaches.
Closing Thoughts
Exportable audit logs are more than a record, they are proof of control, accountability, and transparency. Integrated with SIEM dashboards and standardized across Office 365, Azure, AWS, Linux, and collaboration tools, they transform audit preparation from a scramble into a structured, verifiable process.
By planning, standardizing, and integrating your audit logs, you can confidently deliver evidence, demonstrate operational security, and reduce audit effort.


