Imagine if every employee in the Fortune 100 had their credentials compromised twice over. That’s the scale of this breach: 16 billion credentials exposed, aggregated from thirty datasets, some over 3.5 billion entries each. These weren’t legacy dumps—many are fresh logs from infostealer campaigns.
B2B services—especially VPNs, SaaS platforms, and DevOps tools—were affected. Infostealer malware thrives as long as people store passwords in browsers or reuse credentials. And this isn’t about Fancy headline breaches anymore. Infostealers offer baked-in harvesting abilities: form-grabbing, token theft, screenshot capture, and clipboard scraping.
If you were wondering what infostealer malware is, this breach answers the question. But it also raises a bigger concern: how will your organization prevent becoming the next target?
This blog will unpack:
- How infostealer malware works
- Why “infostealer malware bypasses Google Chrome’s security protections”
- What to do now to protect your organization
What Is Infostealer Malware?
Infostealer malware is specifically engineered to rip sensitive data from infected machines—login credentials, cookies, form autofill details, browser histories, and more. Unlike ransomware, it doesn’t lock your files. Instead, it quietly siphons info back to attackers, often without the user ever noticing.
At its heart, malware infostealer evolves fast. New strains use advanced techniques to bypass browser defenses, especially in Chrome. That’s why headlines about infostealer malware bypassing Chrome’s security protections and even infostealer malware threatening Chrome’s security by bypassing defenses are resurfacing.
Put simply:
- The infostealer malware definition includes trojan-like behavior: it arrives via phishing or cracked software, searches browser storage, and pushes out saved credentials.
- It moves deeper then, grabbing session tokens and cookies and even harvesting screenshots and clipboard contents.
Infostealer malware examples are numerous: RedLine, Agent Tesla, Lumma, and the Rust-based Myth variant. Recent campaigns used infostealer malware analysis to see how these tools adapt to MFA protections. Attackers layer in second-stage payloads that mimic legitimate browser processes, then read out storage or hook into running sessions.
So, what makes infostealer malware especially pernicious in 2025? It’s stealth. It doesn’t run as obvious ransomware. Instead, it quietly exfiltrates data, often bypassing simple detection solutions. That makes early detection crucial.
How Infostealer Malware Works (Attack Flow + Components)
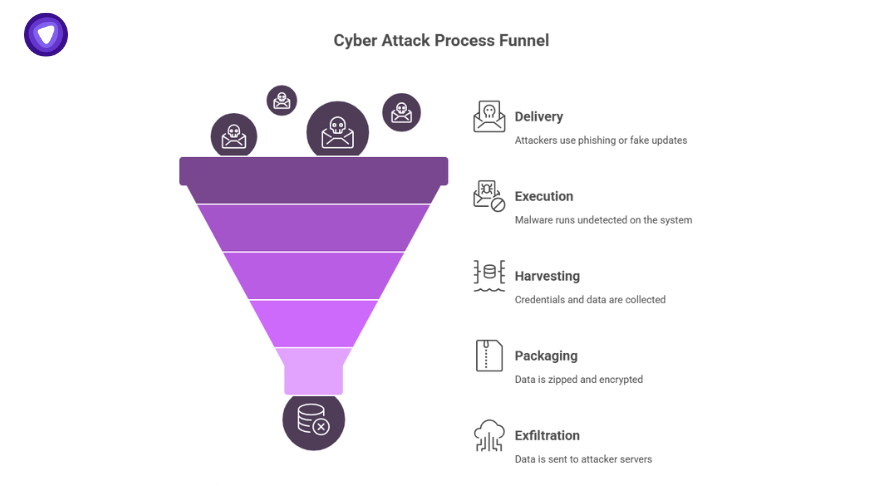
You might wonder: how do attackers actually pull this off? It’s a methodical process:
- Delivery: Phishing emails, fake updates, cracked paywall software
- Execution: Malware runs without alerting users
- Harvesting: Browser credentials, cookies, clipboard data
- Packaging: Zips and encrypts harvested items
- Exfiltration: Sends data to cloud servers or attacker infrastructure
- Resale: Data sold on dark web forums or bundled in credential combos
Infostealer-as-a-service is booming. Operated like SaaS, attackers rent out malware kits and support tools for newbies. At the center are names like infostealer malware examples Lumma, RedLine, Agent Tesla, and newer threats in development.
Each strike collects thousands—sometimes millions—of credentials in minutes. Then those passwords flow into massive dumps, like 16B-credential dataset. It’s brutal efficiency.
Infostealer Malware Bypasses Chrome’s Security—Why That Matters?
Recent reports show infostealer malware bypasses Google Chrome’s security protections, including sandboxing and credential encryption. That’s no small oversight.
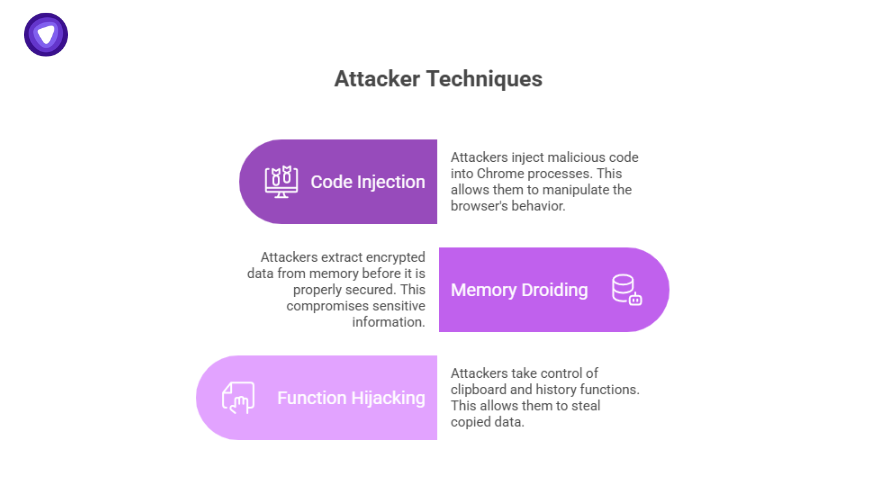
Attackers are using techniques like:
- Code injection into Chrome processes
- Droiding memory to extract encrypted data before it’s secured
- Hijacking clipboard and history functions
In short, infostealer malware threatens Chrome’s security by bypassing defenses we once thought baked in. Some logs even report post-breach token extraction—cookies that remain valid without a password.
B2B systems often rely on browser sessions. If those sessions are vulnerable, the whole perimeter collapses.
So yes—this isn’t theoretical. It’s now happening. And it’s accelerating every few weeks.
Infostealer Malware Detection: What Most Enterprises Miss?
Most SIEM tools flag network anomalies or brute-force attempts, but they miss infostealers almost every time.
Here’s why:
- No brute-force patterns—logins use stolen credentials, so no alerts
- No ransom note or file encryption
- User activity looks normal—within-hours login, same IP ranges
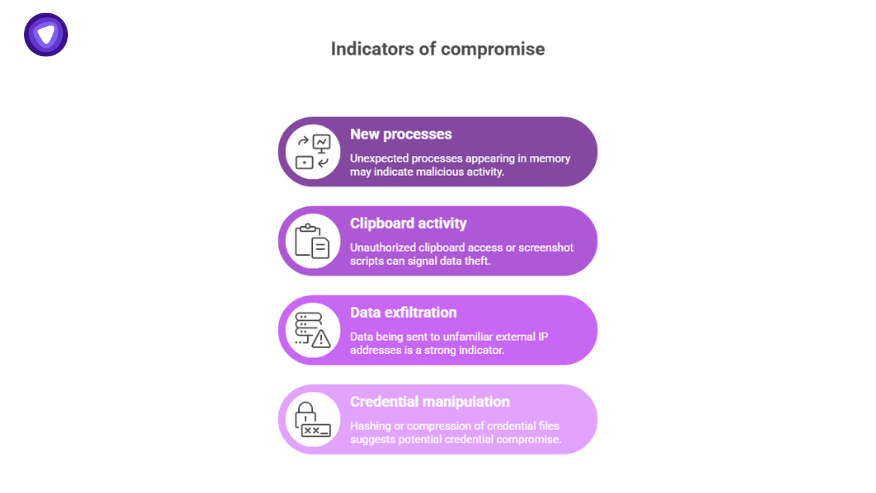
The real indicators are subtle:
- New processes in memory
- Clipboard readings, screenshot scripts
- Data parts being sent to unknown external IPs
- Hashing or compression of credential files
These are IoCs that most teams overlook. Yes, Infostealer malware detection is possible. But it requires endpoint agents and behavioral analytics, not just logs.
So the real question is: how to detect infostealer malware before it’s too late? Specialized endpoint detection and segmentation solutions are part of that answer, alongside threat hunts and log correlation.
Infostealer Malware Analysis: What 16 Billion Leaked Records Reveal
In-depth infostealer malware analysis of the 16B leak shows astonishing scale:
- 30 datasets, each tens to billions of records (largest hit 3.5B)
- Data structures: URL, login, password, OAuth tokens, cookies
- Affects services like Apple, GitHub, major VPN portals, government systems
This mass data raises several flags:
- Infostealer campaigns are automated at scale
- They hit both consumer and enterprise targets
- They harvest not just passwords but session access (tokens)
- They gather recent, weaponizable records—not just old data
These aren’t random leaks. They suggest a highly organized ecosystem, moving from malware-as-a-service to credential economy. The result? A 24/7 credential pipeline of fresh, poisonous data.
What this shows: Infostealer malware compromised credentials don’t just circulate—they fuel attack chains. A single dataset can harm dozens of enterprises in one credential-stuffing attempt.
Follow us on LinkedIn for case studies, threat intelligence, and zero-trust insights that help you stay ahead of infostealers.
Industry-Specific Risks: Who’s at Highest Risk Right Now?
Some sectors are especially vulnerable:
| Industry | Why It Matters |
| Finance | High-value logins—bank portals, trading platforms, client apps |
| Healthcare | EHR and insurance systems—lots of sensitive personal data |
| SaaS/Tech | Dev-ops keys, CI/CD tools, GitHub—high-value credentials |
| Legal | Case management tools containing legal documents and strategy |
Infostealers don’t discriminate. Their target list includes any saved session or cookie. Once credentials are out, attacker bots scan public and enterprise services—even niche B2B portals.
High-frequency issues:
- Business password reuse
- Shared credentials in team tools
- Inadequate network segmentation
That’s how a single dataset can hit multiple targets across your tech stack.
Business Costs and Brand Fallout
These breaches aren’t just technical issues. They’re existential threats. Consider:
- Identity theft and fraud
- Regulatory fines (e.g. GDPR, HIPAA, SOX)
- Client trust erosion
- Legal exposure and SEC reporting
- Downtime, forensic costs, and PR management
Browser-stored passwords plus poor network segmentation is a recipe for disaster. High-profile infostealer incidents now include leaked healthcare passwords and compromised law firm credentials. Each brings a reputational price far above any payday.
How to Protect Against Infostealer Malware?
Here’s a solid checklist:
- Never store passwords in browsers. No autofill. No exceptions.
- Enable phishing-resistant MFA—FIDO2 keys or enterprise tokens
- Monitor for cookie/session token theft across networks
- Adopt a standalone password manager—no browser hooks
- Re-authentication on high-risk tasks (downloads, SSO)
- Deploy VPN with DNS filtering to block malicious C2 communications
Many teams ask: how to protect against infostealer malware? Utilize layered defenses, including endpoint protection, access control, session monitoring, and encryption. Pair these with secure tools and rotate credentials regularly.
Want real-world strategies to combat threats like infostealer malware? Join our Reddit community to learn from other B2B leaders, troubleshoot issues, and share tactics.
Why PureVPN’s Password Manager Is Built for This?
Defending against infostealer malware requires layered access control and credential hygiene. That’s exactly why PureVPN offers a password manager solution.
What this setup gives you:
- Branded VPN access that isolates privileged sessions and blocks malware C2 channels
- Password manager with no browser integration—credentials stay off endpoints
- SAML/OIDC integration for unified identity management
- API/SDK deployment in under a month
- Encryption at rest and in transit, compliant with SOC2, GDPR
- SIEM-friendly logs for all session and credential activity
In practical terms:
- Malware on your endpoint won’t find credentials stored outside browsers
- VPN channels reduce credential exposure and limit unauthorized access
- You retain full control over where and how sessions are used
This isn’t a stopgap. It’s enterprise-ready, scalable protection—all under your brand.
Don’t Wait for the Next Leak
Infostealer malware is not going away. It’s growing faster, targeting remote workers and B2B platforms every week. The 16 billion credential leak shows how fast these campaigns scale—and how fragile our current defenses are.
Speed and visibility matter. Too often, we rely on browser storage, assume MFA is enough, or ignore endpoint hygiene. That’s a mistake. Every breach window is an opportunity for attackers.
Ready to act?
PureVPN puts secure access and credential hygiene in your hands—branded under your name, ready in weeks. Our VPN and password manager combo eliminates browser-based password risk and secures remote access. No fluff, no noise—just enterprise-ready protection.
Don’t wait for your dataset to become part of the next leak.
Deploy PureWL and put your defenses back on your terms—where they belong.


