Imagine a thief trying every possible key until one finally opens a lock. That’s how brute force attack works, which is a trial‑and‑error method used by hackers to guess login credentials, encryption keys, or secret codes until they strike the correct one.
While simple in concept, when automated with bots and distributed networks, brute force becomes a powerful weapon.
What Is a Brute Force Attack?
A brute force attack is a cybersecurity threat where an attacker systematically tries every combination of characters until they find the correct password to access an account, system, or encrypted data.
Unlike more sophisticated exploits, brute force doesn’t take advantage of a vulnerability, it relies on repetition and computing power to succeed.
How Do Brute Force Attacks Work?
Here’s the step‑by‑step breakdown:
1. Target Selection
The attacker chooses a system entry point:
- VPN login portal
- SSH or RDP remote access
- Web app login
- Email or cloud account
2. Credential List or Wordlist
They use either:
- A wordlist (common passwords like “123456” or “password”)
- A dictionary of guesses
- AI‑generated guesses based on known patterns
3. Automated Tools
Using automated tools, bots repeatedly send login attempts until they hit the right username‑password combo.
4. Exploitation
Once successful, the attacker gains unauthorized access, often without being detected immediately.
This attack method is powerful because it scales: with enough computing power and time, most weak or predictable passwords can be broken.
Recent Brute Force Attack Highlights
Brute force attacks aren’t just theoretical, they’re happening everywhere, targeting everything from VPNs to Linux servers.
A worldwide brute force campaign used nearly 2.8 million IP addresses daily to guess credentials on VPN devices and firewalls from vendors such as Palo Alto Networks, Ivanti, and SonicWall.
The GoBruteforcer botnet is aggressively targeting 50,000+ Linux servers, bruteforcing weak passwords on services like FTP and phpMyAdmin.
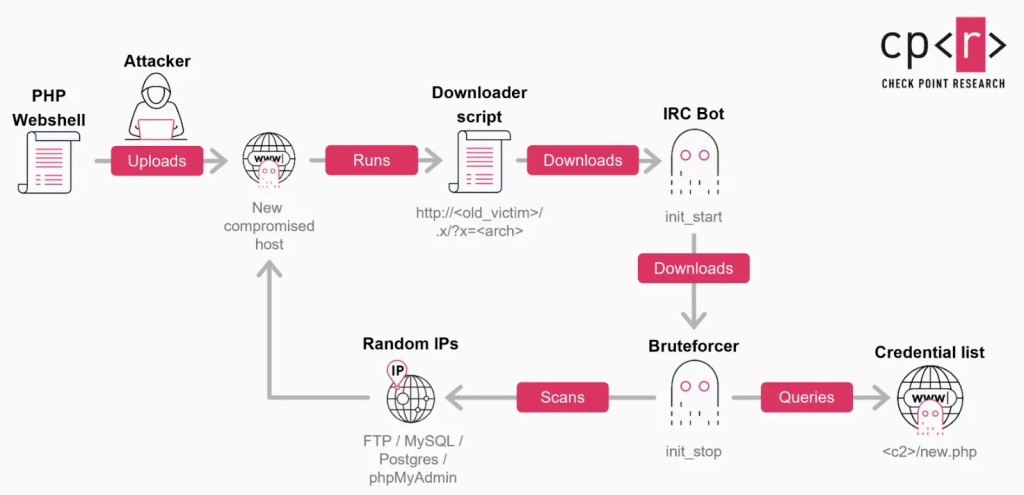
Security researchers reported spikes in brute force attacks against Fortinet SSL VPNs and related remote access systems, with attacks coming from hundreds of malicious IPs.
According to a recent analysis published by Security Magazine, attacks leveraging brute force techniques grew by approximately 12 % in 2024 compared with the previous year.
Improperly configured cloud environments, such as misconfigured storage or weak remote authentication settings, have made it easier for attackers to find entry points and launch large‑scale brute force campaigns. These campaigns often use automated tools that systematically try common passwords or leaked password lists against exposed services like SSH, RDP, or VPN portals.
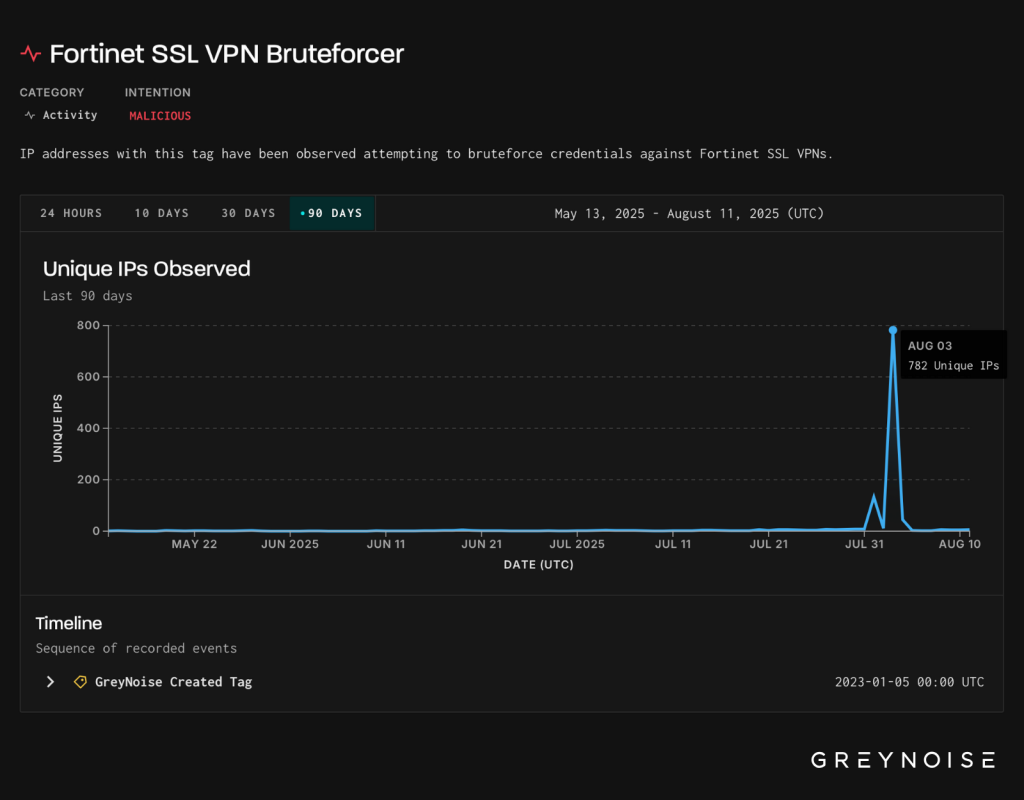
According to recent community data shared on Reddit, backed by Wordfence’s internal statistics, Wordfence, one of the most widely deployed security plugins, reportedly blocked over 19.2 billion brute force attacks in Q3 2025 alone, a 98.9 % increase from the previous quarter. That surge highlights not only the volume of attacks but also how aggressively attackers are scanning and hammering WordPress login pages across the internet.
Shadowserver and Cisco Talos confirm that millions of IPs are participating in brute force login attempts, showing how attackers use distributed methods to avoid easy blocking. Analysts have also highlighted that brute force attacks remain popular because many systems still rely on weak or default passwords and lack strong authentication controls.
Types of Brute Force Attacks and How Do They Differ?
Not all brute force attacks work the same way. While the end goal is always unauthorized access, attackers use different techniques depending on speed, data availability, and the target system.
| Type of Brute Force Attack | How It Works | How It Differs / Key Risk |
| Simple Brute Force Attack | The attacker tries every possible password combination until one works. | Slow but effective against very short or weak passwords. |
| Dictionary Attack | Uses a predefined list of common passwords instead of random combinations. | Faster than pure brute force; relies on predictable human behavior. |
| Credential Stuffing | Tries leaked username‑password pairs from past breaches on other websites. | Extremely effective due to password reuse across services. |
| Hybrid Brute Force Attack | Combines dictionary words with numbers or symbols (e.g., Password123). | Targets slightly stronger passwords with common patterns. |
| Reverse Brute Force Attack | Uses one common password and tries it against many usernames. | Works well when users rely on default or reused passwords. |
| Rainbow Table Attack | Uses pre‑computed hash tables to crack encrypted passwords. | Faster than live guessing but requires stolen password hashes. |
| Distributed Brute Force Attack | Launches attacks from thousands or millions of IP addresses. | Harder to detect and block due to its global, bot‑driven nature. |
| Credential Spraying | Tries one weak password across many accounts slowly. | Avoids lockout detection while exploiting common passwords. |
Top Ways to Prevent Brute Force Attacks
Prevention is a shared responsibility between users and organizations. Here’s how to stay ahead:
1. Strong, Unique Passwords
Use complex passphrases with:
- Upper & lowercase letters
- Numbers
- Special characters
Avoid common patterns and reused passwords across services.
2. Multi‑Factor Authentication (MFA)
Add a second verification step, like an SMS code or authentication app, to significantly reduce the chances of attackers gaining access even if they crack your password.
3. Limit Login Attempts
Set rules to lock accounts or throttle login requests after repeated failures. This defeats automated tools.
4. CAPTCHA & Bot Detection
CAPTCHA challenges and bot mitigation systems make it harder for automated brute force attacks to succeed.
5. Monitoring & Alerts
Real‑time monitoring can flag unusual login activity (e.g., thousands of failed attempts from one source) and let you act fast.
6. Secure Password Storage
Encrypt and hash stored passwords using modern algorithms like bcrypt or Argon2 to prevent breaches from exposing real passwords.
7. Use VPN for Remote Access
Remote access endpoints are frequent brute force targets. Securing them behind PureVPN minimizes exposure and adds a strong authentication layer.
How to Know if Your Data is Compromised in a Brute Force Attack
You won’t notice immediately, but there are clear signs that indicate a compromise. Recognizing these early can help you act quickly to protect your data and prevent further damage.
1. Unusual Login Activity
Check for signs like:
- Login attempts from unknown locations or devices.
- Multiple failed login notifications in your email or app.
- Sudden password change requests you didn’t initiate.
Tip: Many services like Gmail, Outlook, and WordPress log login history, review it regularly.
2. Unexpected Account Lockouts
Repeated failed attempts can trigger automatic lockouts. If your accounts start locking themselves, it could be a sign that someone is attempting a brute force attack.
3. Alerts from Security Tools
Modern antivirus, security suites, or password managers can alert you if:
- Your credentials are part of a known breach.
- Suspicious login patterns are detected.
PureVPN’s breach monitoring can tell if your username/email has appeared in leaked databases.
4. Strange Activity Within Accounts
Signs of compromise include:
- Emails sent you didn’t write.
- Unauthorized purchases or subscriptions.
- Files deleted, downloaded, or shared without your consent.
5. Performance or System Alerts
In some cases, brute force attacks target server accounts (like SSH or RDP). Signs include:
- Server logs showing high numbers of failed login attempts.
- Unexplained spikes in CPU/network usage.
7. Sudden Spam or Phishing
Compromised accounts are often used to send phishing emails or spam. Receiving unusual messages from your own account or seeing suspicious activity in your sent items can indicate compromise.
Frequently Asked Questions
Not entirely, but strong passwords, MFA, and security policies can make them impractical and ineffective.
Yes. Unauthorized access attempts are illegal in most jurisdictions and can result in severe penalties.
That depends on password complexity and computing power. Simple passwords can be cracked in seconds; long, random passphrases could take centuries.
A VPN helps by hiding your public connections and reducing direct exposure of login interfaces, making it harder for attackers to reach your systems.
Absolutely. PureVPN password manager helps you create and store high‑entropy passwords, reducing the likelihood of brute force success.
Conclusion
Brute force attacks might seem simple, guess and check, but when executed at scale with automation and distributed networks, they are a serious threat. Attackers continue to exploit weak credentials and exposed services.
With strong passwords, MFA, limiting login attempts, and a reliable VPN, you can drastically reduce your risk.








