Average Revenue Per User (ARPU) has long served as the headline indicator of financial health in the telecom industry. For decades, steady ARPU growth offset subscriber churn and rising infrastructure costs. That balance has broken.
Mobile markets are near full penetration. Broadband connections are stable but not expanding fast enough to support the cost of new spectrum, fiber, and 5G deployments. Usage volumes keep rising, yet revenue per user is mostly static. This creates a structural imbalance: operators face higher network costs without proportional revenue growth.
Telecom leaders now confront a difficult reality. Traditional service lines alone cannot fund future networks or deliver sustainable profit. Diversification into new revenue streams is becoming the only viable way to protect margins and extend customer lifetime value.
- Stalled growth: ARPU growth has plateaued in most mature telecom markets despite rising usage.
- Margin squeeze: Price-based ARPU gains are offset by cost growth, shrinking contribution margins.
- Strategic shift: Diversification into higher-value services is now a survival strategy, not optional.
- Growth areas: Security, private 5G, enterprise connectivity, cloud, fintech, and digital content bundles.
- Fast entry: White label services like VPN and password managers let operators join these categories without building infrastructure.
Global Telecom Market Overview
The global telecom market is valued at around USD 1.8–2 trillion and is projected to grow slowly through 2030. The sector faces rising operational costs, intense price competition, and heavy capital expenditure from 5G rollouts.
Telecom ARPU growth 2025 is expected to remain low in mature markets due to saturation and aggressive competition. While demand for data continues to expand, pricing pressure from over-the-top services limits monetization.
Telecom trends 2025 show operators focusing on network optimization, automation, and operational efficiency to preserve margins.
Telecom trends 2030 forecast a shift from consumer data bundles to enterprise-centric revenue streams such as private 5G networks, network slicing, and managed cloud connectivity.
This creates a new industry dynamic: top-line revenue can grow only through product diversification, not user growth. Without new services, ARPU stagnates while cost bases expand.
Why ARPU Growth Has Stalled?
ARPU growth is slowing because several structural drivers have weakened.
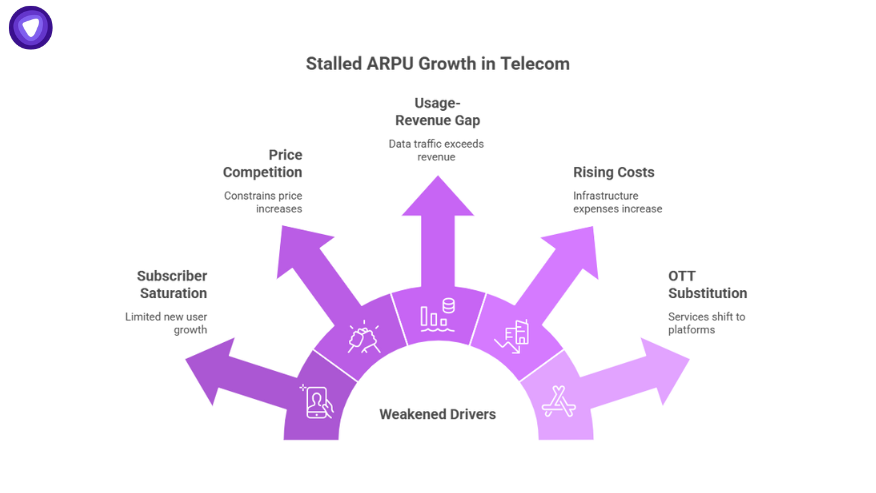
- Subscriber saturation
Mobile penetration in most developed markets has reached 90–120 percent, limiting new user growth.
- Price competition
Intense competition constrains price increases. Even when operators raise prices, churn risk offsets gains.
- Usage-revenue gap
Data traffic is rising faster than revenue. Price per gigabyte is falling each year, lowering monetization rates.
- Rising infrastructure costs
5G spectrum, network densification, and fiber buildouts increase costs. ARPU is not rising fast enough to cover these expenses.
- Over-the-top substitution
Messaging, voice, and video services are shifting to third-party platforms, reducing telecom control of user spend.
As these factors converge, traditional ARPU-focused strategies can no longer sustain long-term profit.
Why Diversification Is Now the Only Path to Sustainable ARPU?
In current conditions, ARPU alone no longer reflects business health. High ARPU in a low-margin product can still damage profitability. Operators now need services that increase both revenue per user and gross margin.
Diversification creates this dual impact. By bundling value-added services, operators increase customer lifetime value, raise switching costs, and protect their base from competitive pricing attacks.
Growth-aligned categories include:
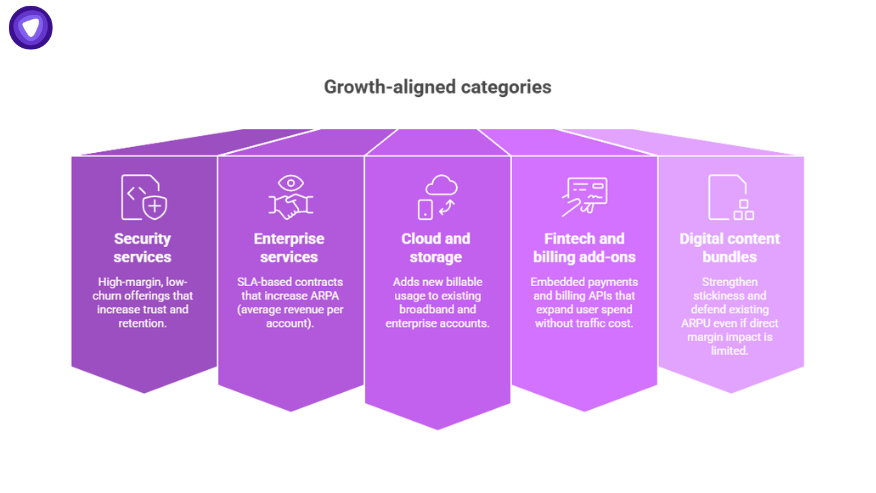
- Security services (VPN, password management): High-margin, low-churn offerings that increase trust and retention.
- Enterprise services (SD-WAN, private 5G): SLA-based contracts that increase ARPA (average revenue per account).
- Cloud and storage: Adds new billable usage to existing broadband and enterprise accounts.
- Fintech and billing add-ons: Embedded payments and billing APIs that expand user spend without traffic cost.
- Digital content bundles: Strengthen stickiness and defend existing ARPU even if direct margin impact is limited.
This transition marks the shift from being access providers to becoming platform operators with multiple revenue streams per customer.
ARPU and Margin: Measuring What Actually Matters
ARPU must be paired with margin data to guide strategy. A useful operator metric is Contribution Margin Per User (CMPU):
CMPU = (ARPU × Gross Margin %) – Support Cost Per User
This formula accounts for both revenue and the costs of serving each customer. It reveals when high ARPU segments are unprofitable due to high acquisition or support costs.
CMPU Calculator
It also highlights the value of bundling. Adding services like VPNs or cloud storage raises ARPU with almost no additional network cost, increasing CMPU far more effectively than price hikes alone.
Building an ARPU Growth Engine: Operator Playbook
Here’s the step by step guide to building an ARPU growth engine:
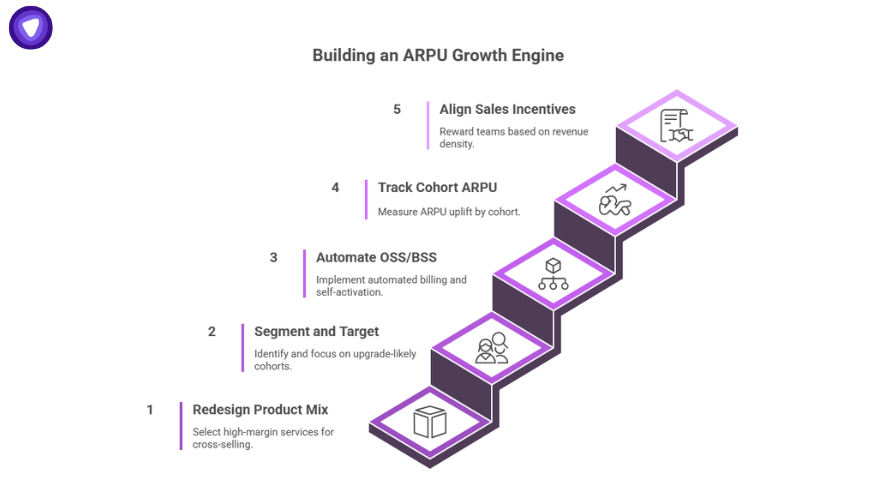
Step 1: Redesign Product Mix
Select high-margin attach-ready services such as VPN, cloud storage, and security packages for cross-selling to the existing base.
Step 2: Segment and Target
Use usage, spend, and churn data to identify cohorts most likely to upgrade. Focus on segments that have stable tenure and low price sensitivity.
Step 3: Automate in OSS/BSS
Create entitlement rules, automated billing flows, and self-activation capabilities to reduce operational friction and scale offers quickly.
Step 4: Track Cohort ARPU
Measure ARPU uplift at the cohort level by acquisition month or customer segment to prove revenue impact.
Step 5: Align Sales Incentives
Reward teams based on revenue density (ARPU × retention) rather than on subscriber count alone to shift sales focus toward profitability.
Case Snapshots: Where ARPU Is Growing?
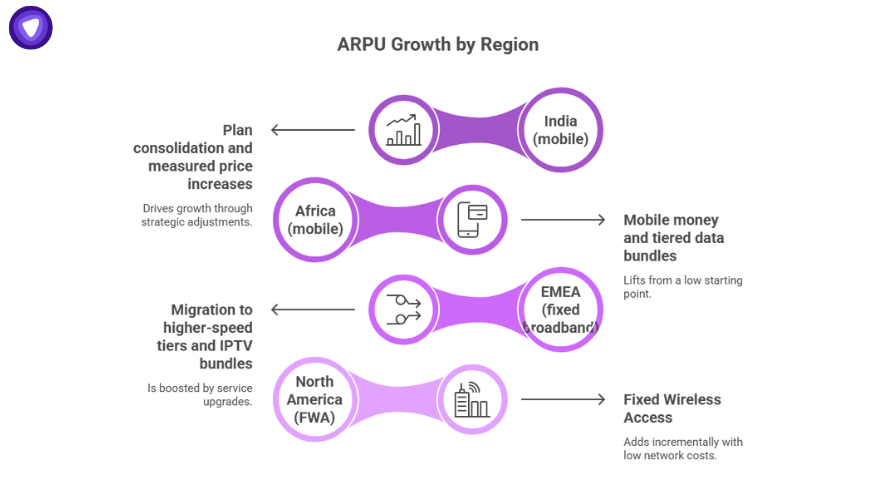
- India (mobile): Operators such as Jio and Airtel have grown ARPU through plan consolidation and measured price increases.
- Africa (mobile): Mobile money and tiered data bundles are raising ARPU from a low base.
- EMEA (fixed broadband): ARPU gains stem from migration to higher-speed tiers and IPTV bundles.
- North America (FWA): Fixed Wireless Access adds incremental ARPU with minimal new network cost.
These regions show that ARPU can grow when operators pair price actions with product expansion and disciplined delivery.
Fast Entry Into High-ARPU Security Services
Security services offer stable ARPU growth and low churn. Building them from scratch is costly, but PureVPN White Label enables telecom operators to launch branded VPN and password management services without developing infrastructure.
Offering these under your own brand increases customer lifetime value, protects ARPU during price competition, and creates a new recurring revenue stream with minimal operational risk.
Conclusion
Telecom ARPU growth is no longer guaranteed. Subscriber saturation, price competition, and rising costs have created a structural revenue gap. Traditional service portfolios cannot sustain profit margins.
Diversification is now a survival strategy. Operators must introduce security, enterprise connectivity, cloud, fintech, and content services to raise revenue per user and protect contribution margins.
White label services such as VPN and password managers allow operators to enter these categories quickly. They raise ARPU without adding cost burden. Building a broader service mix is the clearest path to long-term growth in the telecom sector.


