Cybercriminals no longer rely only on ransomware to cause damage. Information-stealing malware is now a preferred choice, and Vidar is among the most active threats in this category.
Vidar malware is designed to harvest data silently. It extracts browser credentials, session cookies, cryptocurrency wallets, and even tokens used to log into enterprise SaaS platforms. Once stolen, this information is sold on underground markets or used for secondary attacks, including ransomware.
For organizations, Vidar is not just a technical threat. It has direct financial and regulatory consequences. This guide explains what Vidar is, how it spreads, how to detect and remove it, and the steps enterprises can take to reduce exposure.
- Threat: Vidar malware is a data-stealing Trojan active since 2018.
- Spread Vectors: Delivered via phishing, malvertising, cracked software, and gaming lures.
- Stolen Data: Passwords, cookies, wallets, SaaS tokens, and system information.
- Detection: Monitor endpoint access to browser databases and unusual network traffic.
- Removal: Isolate devices, rotate credentials, reset MFA, revoke sessions, and rebuild systems.
- Prevention: Apply browser hardening, DNS filtering, application allow-listing, and VPN enforcement.
- Business Value: Use PureVPN White Label to secure remote access, protect SaaS logins, and strengthen customer trust.
What Is Vidar Malware?
Vidar malware is an information-stealing Trojan, sold as Malware-as-a-Service, that targets browsers, crypto wallets, and system data, often delivered through phishing or malicious downloads.
Vidar was first identified in 2018 and is considered a fork of the Arkei stealer. It is widely used because it is easy to obtain on criminal forums and requires little technical expertise to deploy.
Key Capabilities
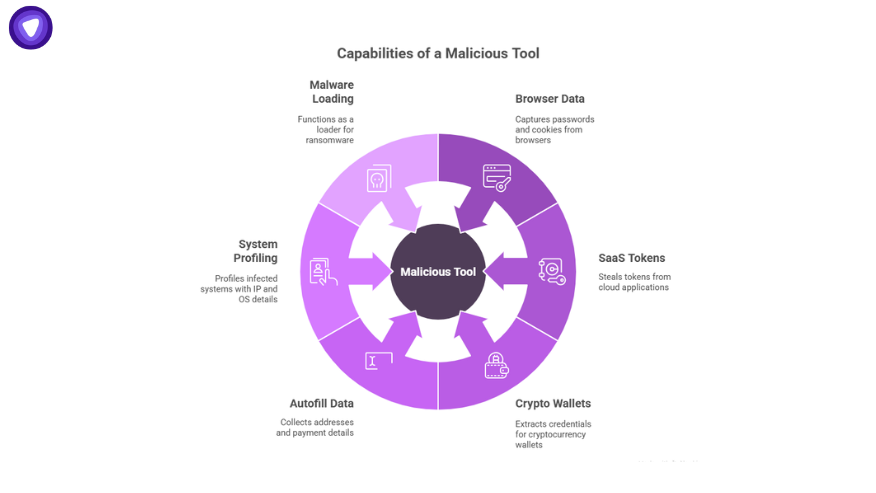
- Captures browser-stored passwords and cookies
- Steals tokens from SaaS apps such as Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, and GitHub
- Extracts cryptocurrency wallets and exchange credentials
- Collects autofill data, including addresses and payment details
- Profiles infected systems (IP, operating system, hardware)
- Functions as a loader, dropping ransomware or other malware
Attackers profit by selling “logs,” packages of stolen credentials and cookies. Buyers then use these for account takeovers, fraud, or as an entry point to larger corporate networks.
How Vidar Malware Spreads?
Vidar adapts to whatever distribution channel is most effective. Recent campaigns have shown several consistent methods:
- Phishing emails with malicious attachments or links
- Malvertising campaigns using poisoned search ads
- Cracked software downloaded from torrents or warez sites
- Fake utilities impersonating trusted software like Sysinternals tools
- Gaming lures including trojanized Steam titles
The infection path changes, but the goal remains constant: gain access to a host through common user behavior.
Why Vidar Is a Business Threat?
Vidar avoids attention. Unlike ransomware, it does not announce its presence by encrypting files. It operates quietly, exfiltrating data until accounts are compromised or customer data surfaces for sale.
Business Impact
- Financial loss: drained wallets and unauthorized transfers
- Account takeovers: SaaS access abused by attackers
- Ransomware deployment: Vidar logs often resold to ransomware operators
- Reputation damage: customers lose confidence after credential theft
- Compliance violations: regulatory fines for exposed PII or PCI data
For MSPs, ISPs, and SaaS platforms, a single infection can escalate into client-wide compromise.
How Vidar Malware Works?
Kill Chain Overview
| Stage | Description | Example Tactics |
| Initial Access | Infection through phishing or fake ads | Malicious attachments, drive-by downloads |
| Execution | Trojanized executables and loaders | PowerShell, rundll32 abuse |
| Collection | Steals credentials, cookies, wallets | Browser DB scraping, keylogging |
| Exfiltration | Sends data to remote servers | HTTP POST, Discord or Telegram channels |
| Monetization | Data resold or used in ransomware ops | Credential stuffing, extortion |
Vidar’s resilience comes from its use of commodity packers, encryption for exfiltrated data, and constant infrastructure rotation. These factors make it harder to detect with traditional antivirus alone.
Signs of a Vidar Infection
Technical Indicators
- Unknown processes imitating Windows executables
- Suspicious access to browser credential databases
- Outbound HTTP POST requests to unusual domains
- TLS traffic with uncommon signatures
- Abnormal data transfer volumes
User Indicators
- Unexplained multi-factor authentication prompts
- Cloud accounts accessed from unexpected locations
- Cryptocurrency wallet balances dropping without direct compromise
Table: Warning Signs for IT Teams vs Employees
| IT Teams | Employees |
| Abnormal DNS and TLS connections | SaaS account lockouts or unfamiliar logins |
| Browser database access anomalies | Wallet balances disappearing |
| Large POST requests to new IP ranges | Unexpected password reset notifications |
Detecting Vidar in Enterprise Systems
Effective detection requires monitoring across endpoints and networks:
- Endpoint monitoring: flag attempts to access browser credential stores
- EDR and AV updates: use signatures that track recent Vidar samples
- Network analysis: detect beaconing or suspicious POST traffic
- Threat intelligence feeds: monitor known C2 domains and hashes
- Dark web monitoring: check log shops for credentials linked to your domain
Organizations without internal SOC resources should consider external managed detection services to maintain coverage.
Removing Vidar Malware
A disciplined response is critical once Vidar is suspected.
Incident Response Checklist
- Isolate affected endpoints from the network
- Rotate all credentials stored on infected devices
- Reset and re-seed MFA tokens
- Revoke OAuth tokens and active SaaS sessions
- Reissue API keys and developer tokens
- Rebuild or wipe compromised devices
- Monitor dark web forums for stolen credentials
Skipping steps risks leaving attackers with valid tokens or session cookies that bypass password resets.
Preventing Vidar Infections
Technical Measures
- Disable browser password storage; enforce enterprise password managers
- Apply application allow-listing to block unauthorized executables
- Use DNS filtering to prevent connections to malicious domains
- Patch software promptly to close loader vulnerabilities
Organizational Measures
- Educate employees about phishing, malvertising, and cracked software risks
- Audit vendor practices to ensure no unnecessary data is exposed
- Conduct regular credential hygiene audits
Strategic Measures
- Require VPN access for all remote employees
- Adopt zero-trust authentication for SaaS platforms
How PureVPN White Label Helps Contain the Risk?
Vidar relies on stolen credentials and insecure connections. While training and monitoring are vital, enterprises must also ensure all data in transit is protected.
PureVPN White Label enables businesses to:
- Deploy branded VPN services to employees and clients
- Secure SaaS and VDI logins with strong encryption
- Add a new recurring revenue line while improving security posture
- Reinforce customer trust by offering security under their own brand
By combining malware detection with encrypted access, organizations reduce the chance of Vidar logs being harvested or resold.
Conclusion
Vidar malware is a leading example of how quiet data theft can be more damaging than loud ransomware events. It compromises accounts, drains assets, and opens doors for larger attacks.
Organizations that treat Vidar as a low-level nuisance risk financial losses, compliance penalties, and loss of customer confidence.
By combining robust monitoring with strong preventive measures, businesses can reduce their exposure. With PureVPN White Label, you gain the added ability to deliver encrypted, branded VPN services to your workforce and clients. This strengthens security and creates new business value.


