Few things are more frustrating than trying to access a website and being greeted by a 502 Bad Gateway error. Whether you’re a website visitor, business owner, developer, or IT admin, this error can disrupt traffic, impact user trust, and even cost revenue.
If you’ve recently seen messages like, 502 Bad Gateway Nginx, 502 Bad Gateway Cloudflare, HTTP Error 502, 502 Server Error: The server encountered a temporary error. You’re not alone! Let’s break down what a 502 Bad Gateway error really means, why it happens, and how to fix it quickly.
What Is a 502 Bad Gateway Error?
A 502 Bad Gateway error is an HTTP status code that indicates one server on the internet received an invalid response from another server. In simple terms, a gateway or proxy server tried to get data from an upstream server but didn’t receive a proper response.
Most modern websites use multiple servers:
- A client (your browser)
- A gateway server (like Nginx, Apache, or Cloudflare)
- An upstream server (application server, API server, or backend system)
If the gateway can’t successfully communicate with the backend server, it returns a 502 error.
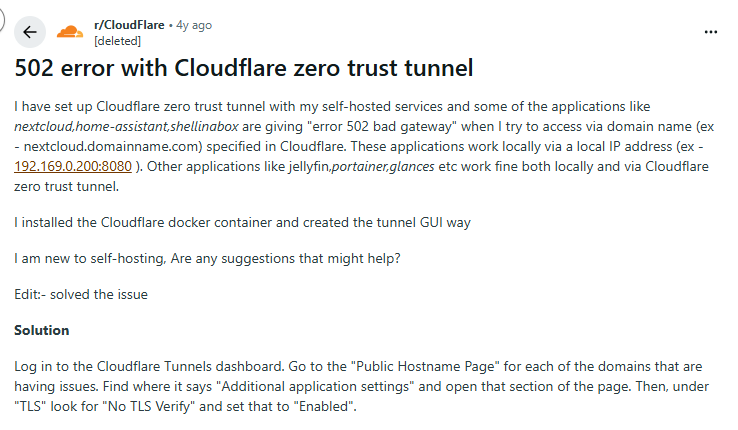
Common Causes of a 502 Bad Gateway
Understanding the root cause is key to fixing the issue.
1. Server Overload
If a website receives too much traffic, the backend server may crash or become unresponsive.
This often happens during:
- Product launches
- Flash sales
- Viral traffic spikes
- DDoS attacks
2. Server Downtime or Crash
If the upstream server is down entirely, the gateway has nothing to communicate with. Common reasons include:
- Misconfigured updates
- Application crashes
- Expired services
- Resource exhaustion (RAM/CPU limits)
3. DNS Issues
Incorrect DNS settings can cause servers to fail when routing traffic. You might see 502 errors when:
- Migrating to a new host
- Changing CDN providers
- Updating nameservers
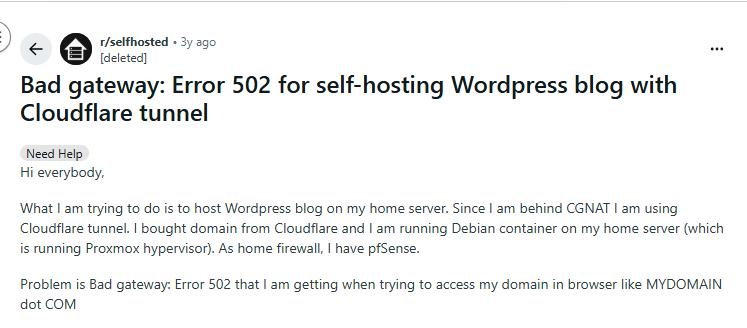
4. Firewall or Security Blocks
Sometimes, security software blocks legitimate server-to-server communication. This can happen due to:
- Strict firewall rules
- ModSecurity rules
- Rate-limiting
- IP reputation filtering
5. Reverse Proxy Misconfiguration
If you’re using:
- Nginx
- Apache
- HAProxy
- Cloudflare
Improper configuration like incorrect port mapping or timeout settings can trigger 502 errors. This is one of the most common issues discussed in threads.

502 Bad Gateway vs Other HTTP Errors
It’s important not to confuse 502 with similar errors.
| Error Code | Meaning |
| 500 | Internal server error |
| 503 | Service unavailable |
| 504 | Gateway timeout |
| 502 | Invalid response from upstream server |
A 504 timeout means the upstream server didn’t respond in time. A 502 means it responded incorrectly or not at all.
How to Fix 502 Bad Gateway (For Website Visitors)
If you’re simply trying to open a website and run into a 502 Bad Gateway error, don’t panic. In many cases, the issue is temporary and can be resolved with a few quick troubleshooting steps.
Here’s what you can do:
1. Refresh the Page
Start with the simplest fix. Press F5 or click the refresh button.
A 502 error is often caused by temporary server overload. If the backend server was briefly overwhelmed, a reload after a few seconds may connect you successfully once traffic stabilizes.
2. Clear Your Browser Cache
Corrupted or outdated cached files can interfere with how your browser loads a website. Clear your:
- Browser cache
- Cookies (optional if issue persists)
Then try accessing the site again in a fresh session.
3. Try a Different Browser or Device
Switching browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Edge, Safari) or using another device helps determine whether the issue is:
- Browser-specific
- Device-specific
- Network-related
If the website works elsewhere, the problem is likely local to your setup.
4. Flush Your DNS Cache
Sometimes your system is holding onto outdated DNS records, which can interfere with server routing.
On Windows:
ipconfig /flushdns
On Mac:
sudo dscacheutil -flushcache
After flushing DNS, restart your browser and try again.
5. Switch Networks or Use a Secure VPN Connection
If the website still isn’t loading, your network could be the issue. Across tech forums and Reddit discussions, users frequently report situations like:
“The site works on mobile data but not on my home Wi-Fi.” This usually points to:
- ISP-level routing issues
- Regional CDN outages
- IP-based restrictions or temporary blocks
In these cases, switching from Wi-Fi to mobile data (or vice versa) can immediately confirm whether the problem is network-specific.
Using a secure VPN connection can also help diagnose the issue. By routing your traffic through a different server and location, a VPN allows you to determine whether the 502 error is tied to your ISP, geographic region, or IP address.
If the site loads when connected through a different server route, the problem is likely regional, not a complete website outage.
How to Fix 502 Bad Gateway (For Website Owners)
If you manage a website or server, troubleshooting might be tricky:
Step 1: Check Server Status
Verify if:
- Your application server is running
- Services like PHP-FPM are active
- Backend APIs are responding
Restarting services often resolves temporary crashes.
Step 2: Check Error Logs
Look into:
- Nginx logs
- Apache logs
- PHP error logs
- Cloudflare logs
You may see errors like:
- connect() failed (111: Connection refused)
- upstream prematurely closed connection
These points lead to backend failure.
Step 3: Increase Server Resources
If memory or CPU usage spikes, consider:
- Scaling vertically (more RAM/CPU)
- Using auto-scaling infrastructure
- Upgrading hosting plans
Many WordPress users report 502 errors resolving after moving from shared hosting to VPS.
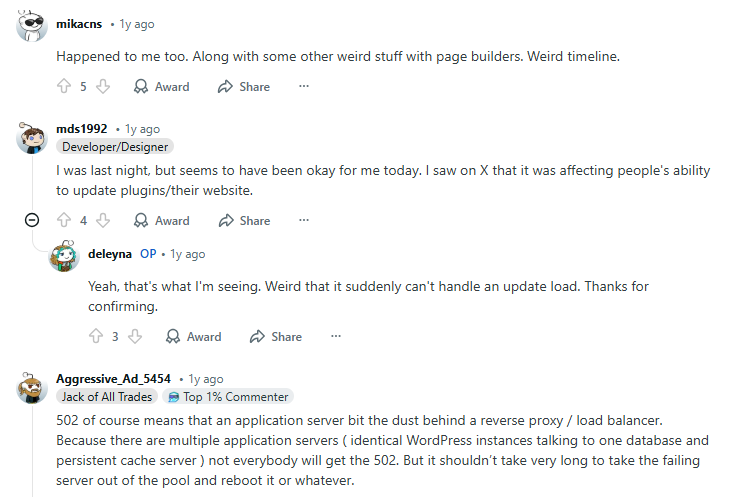
Step 4: Check Firewall and Security Rules
Temporarily disable:
- ModSecurity
- WAF rules
- Rate-limiting
Then test connectivity. If the issue resolves, adjust rules instead of leaving protection off.
Step 5: Review Reverse Proxy Configuration
Check:
- Proxy timeout values
- Port settings
- Upstream server IPs
- SSL/TLS settings
Even a small typo in configuration files can trigger 502 errors.
Step 6: Check for DDoS or Malicious Traffic
Heavy malicious traffic can overwhelm backend servers. Using layered protection (CDN + firewall + secure tunneling) reduces risk.
If your infrastructure serves remote teams or backend dashboards, pairing secure network access with encrypted VPN connections adds another layer of protection against traffic manipulation and routing interference.
Preventing 502 Errors in the Future
Preventing 502 errors isn’t about a single fix, it’s about building a reliable, secure, and scalable infrastructure.
1. Use Real-Time Monitoring Tools
You can’t fix what you can’t see. Set up performance monitoring and automated alerts for:
- CPU spikes
- Memory usage thresholds
- Disk I/O saturation
- Server downtime
- Slow response times (latency monitoring)
Tools like server monitoring dashboards, uptime monitors, and APM (Application Performance Monitoring) platforms help you detect backend instability before it turns into a visible 502 error. Early detection allows you to restart services, scale resources, or reroute traffic before users are affected.
2. Implement Load Balancing
Relying on a single backend server is risky. Load balancing distributes incoming traffic across multiple servers, ensuring that:
- No single machine becomes overwhelmed
- Traffic spikes are absorbed more smoothly
- If one server fails, others continue serving users
This redundancy reduces the chances of gateway failures and improves overall uptime.
3. Enable Auto-Scaling in the Cloud
Traffic patterns are rarely predictable. Cloud platforms allow dynamic scaling based on demand. When traffic increases:
- New instances spin up automatically
- Resources expand in real time
- Performance remains stable
When traffic drops, resources scale back down, keeping infrastructure efficient and cost-effective. Auto-scaling is critical for e-commerce sites, SaaS platforms, and apps that experience sudden traffic bursts.
4. Secure Your Infrastructure
Security incidents are a hidden cause of 502 errors. DDoS attacks, brute-force attempts, or bot traffic can overwhelm backend services and crash upstream servers.
Protect your infrastructure by securing:
- Admin dashboards
- SSH and server access
- Remote developer connections
- Internal APIs
Using secure network tunnels and encrypted connections reduces backend exposure for distributed teams managing servers remotely. Layered protection (firewalls, WAF, VPN-secured access, and DDoS mitigation) ensures that malicious traffic doesn’t destabilize your application stack. A stable network foundation isn’t just about performance — it’s about resilience.
5. Keep All Software Updated
Outdated software is a common trigger for server instability. Regularly update:
- CMS platforms (like WordPress, Drupal, Magento)
- Plugins and extensions
- Server software (Nginx, Apache, PHP, Node.js)
- Operating system packages
Compatibility issues, deprecated functions, or security vulnerabilities in old versions can cause backend services to fail, resulting in 502 responses. Routine patching and controlled update cycles help prevent avoidable crashes.
Frequently Asked Questions
It means a server acting as a gateway or proxy received an invalid response from an upstream server.
Usually not. Most of the time, the problem lies with the website’s server.
It depends. Temporary overload may resolve within minutes. Server crashes may require manual intervention.
If the issue is caused by ISP routing problems, regional CDN outages, or IP-based restrictions, using a secure VPN connection may help determine whether the error is location-specific. However, if the website’s backend server is down, a VPN won’t fix it.
Not necessarily. Most 502 errors are configuration or server overload issues. However, DDoS attacks can cause backend failures that result in 502 responses.








