Your credentials may be at risk.
Run a free email scan to see if your data has been exposed — no signup needed.
Did you know that over 80% of hacking-related breaches in 2024 involved weak or stolen passwords? (Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report). If that stat made you double-check your password habits, you’re not alone.
In 2025, the best way to keep passwords safe and organized isn’t scribbling them on sticky notes or reusing the same weak password everywhere. It’s smarter—and far more secure—to use a password manager. These digital vaults use military-grade encryption, autofill your credentials, and help you organize everything from login data to backup codes in one secure spot.
Whether you’re juggling work accounts, shopping logins, or streaming services, this guide breaks down why password managers are your best bet for staying safe and sane online this year.
Why Is It Risky to Store Passwords in Your Head or on Paper?
Relying on memory or physical notes to manage passwords may feel simple, but it’s a major security vulnerability. Paper can be lost or stolen, and human memory is prone to error, especially when handling multiple complex passwords.
Passwords should be random, long, and unique. Without a secure storage method, users risk password reuse and weak password habits—both of which hackers can exploit using brute force or phishing techniques.
What Makes a Password Secure Today?
A secure password is long, random, and unique to each account. Ideally, it should contain a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. The more complex and unique it is, the harder it is to guess or crack.
Length increases entropy—or randomness—making brute-force attacks impractical. Password reuse lowers security because one breach can compromise multiple accounts. Secure password creation tools or generators help ensure strong, varied credentials.
How Does a Password Manager Work?
How a Password Manager Works (Step-by-Step)
- Account Creation and Master Password Setup
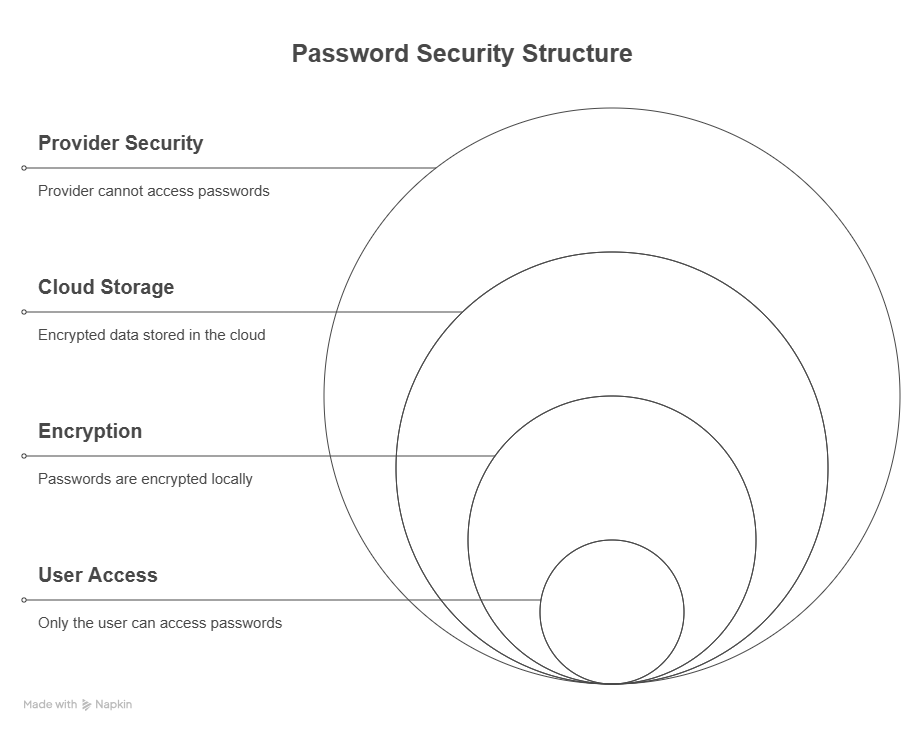
When you set up a password manager, you create one strong master password. This is the only password you’ll need to remember.- This master password is never stored on the provider’s servers.
- It’s used to generate an encryption key locally on your device through a process like PBKDF2 or Argon2 (key derivation functions).
- Encryption of Data
Every password you store is encrypted before it ever leaves your device. The encryption algorithm (usually AES-256) uses the key derived from your master password.- This means even if someone accesses the cloud database, the data is unreadable without the decryption key (which only your device can generate).
- Storing Passwords in the Vault
The encrypted passwords are saved in a digital vault—either on your device or in the cloud.- Each entry (like a Gmail login) is encrypted individually or in groups depending on the manager.
- Synchronization Across Devices (Optional)
If syncing is enabled, the encrypted vault is uploaded to secure servers and downloaded on your other devices.- The encryption key never leaves your devices, ensuring only you can decrypt the data.
- Autofill and Access
When you visit a login page, the password manager:- Matches the URL with saved credentials.
- Prompts for biometric or master password (depending on settings).
- Decrypts the relevant credentials on the fly and autofills them.
- Additional Security Features
- Many password managers support zero-knowledge architecture, meaning the provider can’t see or decrypt anything—even under legal pressure.
- You can enable 2FA (two-factor authentication) for unlocking the vault or even per password entry.
| Rank | Password Manager | Why It’s the Best |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bitwarden | Open-source, highly secure, with robust free and premium plans. |
| 2 | 1Password | Excellent UI, Travel Mode, Watchtower alerts, and strong cross-platform sync. |
| 3 | Dashlane | Premium features like dark web monitoring and a built-in VPN. |
| 4 | KeePass | Offline-only, open-source, fully customizable for advanced users. |
Are Password Managers Really Safe?
Yes, password managers are safe when they use strong encryption protocols like AES-256 and follow zero-knowledge architecture. This means even the service provider cannot view your stored data.
Reputable tools like Bitwarden, KeePass, or PureVPN’s Password Manager undergo regular third-party security audits. Even in rare breaches, encrypted data is often useless to attackers without the user’s master password.
How Can a Password Manager Keep You More Organized?
Password managers categorize your credentials, allowing you to sort them by site type, tags, or folders. You can easily locate or update a login without scrolling through notebooks or spreadsheets.
They also include searchable databases, encrypted notes, and password health reports. Some even notify you of duplicate or weak credentials, streamlining both security audits and day-to-day organization.
What Is the Safest Way to Create and Store a Master Password?
Create a long, unique passphrase that’s easy to remember but hard to guess. Avoid common words or personal information. Use a mix of unrelated words or phrases with numbers and symbols.
- Also Read: Is Google Password Manager Safe to Use?
Store your master password in a secure, offline location like an encrypted USB or password-protected file. Some password managers support biometric unlock as an extra layer of protection.
How Do You Keep Your Passwords Safe from Hackers?
Avoid using public Wi-Fi without a VPN, as unencrypted connections are vulnerable to interception. Hackers can exploit weak or reused passwords via phishing, keyloggers, or data breaches.
Use two-factor authentication (2FA) with your password manager to add a second security layer. Regularly monitor for compromised credentials via dark web scans.
Should You Trust Browser-Saved Passwords?
Browser-stored passwords offer convenience but come with risks. Most browsers lack robust encryption and may auto-fill credentials without verification, making them vulnerable to malware.
Unlike dedicated password managers, browser solutions usually lack 2FA support, audit tools, and advanced organization features. They’re suitable for casual users but not ideal for high-security needs.
How to Combine Password Managers with 2FA for Maximum Protection?
Two-factor authentication (2FA) significantly boosts security by requiring a second step—like a one-time code or biometric scan—to log in. Use 2FA apps like Authy or Google Authenticator alongside your password manager.
Most password managers allow you to store 2FA codes for individual accounts, making it easy to manage both layers of access securely from one app.
Are There Free and Secure Password Managers You Can Trust?
Yes, several free password managers are secure and reliable. Bitwarden offers open-source transparency, cloud syncing, and encrypted vaults. KeePass is great for local-only storage without cloud access.
PureVPN’s bundled password manager adds VPN protection for encrypted network access. Free versions often limit features, but still provide excellent security basics for beginners.
Frequently Asked Questions
Only if your master password is weak. Strong encryption keeps your data secure.
Yes, especially with biometric unlock and device encryption enabled.
Ideally, a unique password for every account. A manager handles them all.
Options like Bitwarden, KeePass, or PureVPN’s tool are all considered secure.
Yes, a VPN encrypts internet traffic and helps keep login sessions secure.