You’re walking into a marketplace where no one uses their real name, every payment is in cryptocurrency, and there’s no way to call customer support if you get scammed. That’s how things work on the dark web. Although it’s all shadowy, people still buy and sell drugs, stolen data, counterfeit goods, and hacking tools. So how do strangers trust each other in a place built on anonymity?
Your email could be compromised.
Scan it on the dark web for free – no signup required.
The answer is escrow, which might feel like something trustworthy, but it’s a mix of clever cryptography, fragile promises, and sometimes outright deception. Law enforcement reports, exit scams, and massive market takedowns have shown that escrow on the dark web isn’t always what it seems.
Let’s discuss in detail how escrow works on the dark web and is it really secure.
What Does“Escrow” Mean on the Dark Web?
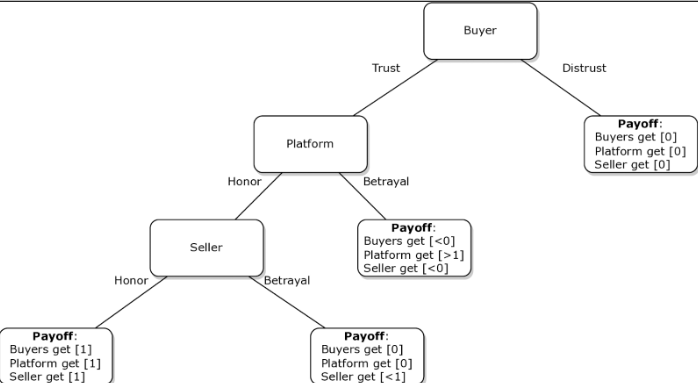
In legitimate commerce, escrow is a neutral third-party that holds payment until agreed-upon conditions are met. On darknet markets and criminal forums, escrow has the same basic function: it holds cryptocurrency (usually Bitcoin or Monero variants) until a buyer confirms receipt or an automated rule releases funds. But the actors, incentives, and technical methods differ, making escrow a trust technology inside a trust-free environment.
Common Escrow Models Used Today
Escrow on the dark web isn’t one-size-fits-all, it comes in different models designed to balance trust and risk.
a) Manual Escrow Agent (Human)
A forum moderator or trusted individual receives funds and later releases them when both parties confirm. This model depends entirely on reputation and social enforcement mechanisms. It was common historically and still exists in smaller communities.
b) Multisignature (multisig) Escrow
A multisig wallet requires multiple private keys to sign a transaction (e.g., 2-of-3). Multisig allows an escrow setup where buyer, seller and escrow server each control a key; funds can be spent only with agreement from two parties. This reduces single-point betrayal risk. Several academic and industry studies point to multisig as a major innovation for market resilience.
c) Automated Smart-Contract / Script Escrow
When markets integrate on-chain or off-chain scripts, funds are released automatically once predefined conditions are detected. On Tor-only markets, full smart-contract use is less common because many prefer privacy coins and off-chain escrow, but hybrid approaches (escrow + on-chain settlement) appear in some forums. Recent technical analyses examine how automation reduces human error but can create new vulnerabilities.
d) Reputation + Review Escrow (Social Escrow)
Some markets make escrow optional but use reputation systems, escrow badges and review penalties to simulate the protective effect of escrow without moving coins into third-party control. These rely on community enforcement and market stability. Studies on social dynamics show this is a powerful but fragile mechanism.
3) Why Criminals Use Escrow — Incentives and Trust Signals
Escrow directly addresses three problems:
- Exit scams / rug pulls: markets or sellers abscond with funds. Escrow reduces immediate loss by holding buyer funds.
- Delivery disputes: escrow provides arbitration (human or algorithmic) to adjudicate claims.
- Reputation signaling: offering escrow (especially multisig/automated) is a costly signal that indicates a market or seller is professional and long-term oriented.
Researchers frame escrow as a costly signalling mechanism: markets that offer safe, reliable escrow attract more volume because buyers are less exposed to opportunistic behavior. However, the signal can be faked (reputation manipulation) and escrow agents can be compromised.
Real-World Data & Trends (2023–2025) — What the Numbers Say
Below are the most load-bearing, up-to-date datapoints about dark web activity and enforcement that directly affect escrow dynamics:
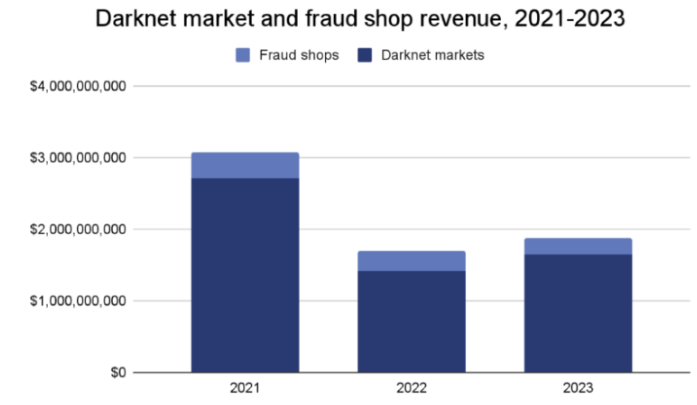
- Market Revenue Rebound (2023)
Chainalysis reported that darknet markets and fraud shops received $1.7 billion in 2023, an increase from 2022, showing that despite takedowns, markets remain lucrative. Higher revenue increases incentives for both more sophisticated escrow and scams.
- Law-Enforcement Takedowns Continue (2024–2025)
Europol’s IOCTA 2024 and subsequent coordinated actions document sustained pressure on marketplaces, seizures and operations that disrupt escrow infrastructures. For example, a major global operation in May 2025 resulted in 270 arrests and seizures of drugs and cryptocurrency, showing that escrow arrangements can become forensic opportunities when markets are disrupted.
- Shifts in Laundering Tools (2022–2024)
Chainalysis documents a decline in funds to classic crypto mixers from illicit addresses (from about $1B in 2022 to ~$504M in 2023) and evolving use of alternative laundering methods. This affects escrow because on-chain traces and mixer use influence both anonymity and the attractiveness of escrow models.

- Academic and Security Research (2024–2025)
Multiple peer-reviewed and technical papers released in 2024–2025 analyze automated escrow, multisig adoption, and trust dynamics, reinforcing that while escrow reduces some scam types, it introduces new attack surfaces (compromised keys, flawed automation).
How Escrow Fails Even On the Dark Web
Escrow is not a silver bullet and could be failed too.
- Compromised Escrow Agent or Admin Access
A trusted human agent (or market admin) runs away with funds or is arrested; if they control keys, coins are gone.
2. Fake Escrow / Phishing Escrow Pages
Attackers impersonate escrow interfaces or send buyers to fake payment flows. Automated scripts can’t protect against off-channel social engineering.
- Multisig Misconfiguration or Key Theft
If multisig keys are exposed orthe signing infrastructure is compromised, funds can be stolen or permanently locked.
- Dispute Bias / Corrupt Arbitration
Human arbitrators can be bribed or coerced; automated arbitration may be buggy or gamed.
- Blockchain Traceability Leading to Law Enforcement
Escrow flows (even with mixers) can create IOCs (indicators of compromise) used by analytics firms and LEAs to map networks and ultimately tie participants to seizures. Chainalysis and DOJ casework show how forensic tracing of escrow flows has helped investigations.
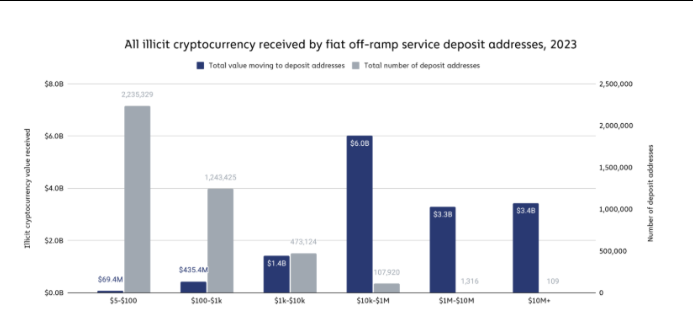
How Escrow Can Help Investigators – Law Enforcement & Analytics
Escrow creates concentrated points of value and therefore, is forensic gold:
- Funds aggregated in escrow wallets provide a smaller set of addresses for analysts to trace.
- Dispute communications (messages, screenshots) are often stored in market logs or backups seized during takedowns.
- Admin accounts or multisig providers, once compromised or subpoenaed, can reveal networks of buyers and sellers. The FBI/DOJ seizures in 2024–2025 and the Europol IOCTA emphasize that takedowns of markets and escrow services yield both asset seizures and intelligence.
At the same time, criminals evolve: they increasingly use privacy coins, off-chain swaps, atomic swaps, and decentralized, ephemeral escrow mechanisms to reduce single points of failure.
Beyond the Hype: What You Should Keep in Mind!
Escrow on the dark web is often misunderstood: it’s a risk buffer, not a safety net. For anyone exploring this space, whether for privacy, defense, or research, the key is to separate myth from reality.
- Understand what escrow does and doesn’t protect. Escrow mitigates counterparty risk but does not make an illegal or risky transaction safe. Treat escrow as a risk-reduction, not a risk elimination tool.
- Think like a defender, if you’re protecting an organization, monitor blockchain patterns for large, recurring escrow addresses, and watch market disruptions as intelligence sources.
- For individual privacy, using PureVPN protects transport-level metadata (your IP, ISP logs), which helps you stay anonymous, but will not anonymize your blockchain transactions or protect you from legal liability. Combining various privacy measures, secure endpoint hygiene, privacy coins, mixing strategies where legal, and operational security, is necessary if privacy is your concern.
Remember, if you are considering using any escrow while using the dark web for legal purposes, prudence and risk analysis are extremely important.
Wrap Up
Escrow on the dark web is a meaningful safety net in that it reduces specific, common attack vectors (seller exit scams, some buyer disputes). But it is not a foolproof shield as escrow centralizes value, which makes it attractive to attackers and law enforcement alike.
Plus, it introduces technical and social failure modes (compromise, impersonation, and arbitration corruption). So, escrow is less a safety net and more a temporary balancing, useful for reducing risk, but never capable of eliminating it.
Frequently Asked Questions
No. Escrow reduces certain fraud risks but introduces new attack surfaces (compromise of escrow keys, biased arbitration) and doesn’t prevent law enforcement tracing.
Multisig significantly lowers single-point failure risk but depends on secure key management and honest participants. If keys are stolen or a key-holder is compelled, and bmultisig can fail.
Yes, market takedowns frequently seize escrow wallets and market logs; those have been used as evidence in investigations and forfeiture actions.








