Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) is no longer just a checkbox exercise. In 2026, enterprises face tighter regulations, rising cyber threats, expanding cloud footprints, and increasing third-party dependencies. That’s exactly why GRC tools have become mission-critical for organizations that want visibility, control, and resilience.
In this guide, we’ll break down what GRC tools are, how they work, why they matter in 2026, and which platforms are leading the market right now, so you can confidently shortlist the right solution.
What Are GRC Tools?
GRC tools are software platforms designed to help organizations manage governance policies, assess and mitigate risk, and maintain regulatory compliance, all from a centralized system.
Instead of tracking risks in spreadsheets, policies in emails, and compliance evidence across disconnected systems, GRC platforms bring everything together into a single source of truth.
At a high level, GRC tools help organizations:
- Identify and assess business, IT, and cyber risks
- Map internal controls to regulatory frameworks
- Automate compliance workflows and reporting
- Monitor third-party and vendor risks
- Maintain audit readiness year-round
What Does GRC Stand for in Governance, Risk, and Compliance?
GRC isn’t three separate disciplines, it’s a connected system.
Governance
Governance defines how decisions are made and who is accountable. It includes policies, procedures, ethics, oversight structures, and leadership responsibilities.
Examples:
- Corporate policies and codes of conduct
- IT governance and cybersecurity governance
- Board oversight and executive accountability
Risk
Risk focuses on identifying, analyzing, and mitigating uncertainties that could impact objectives.
Examples:
- Cybersecurity risk
- Operational and financial risk
- Third-party and vendor risk
- Cloud and data privacy risk
Compliance
Compliance ensures adherence to laws, regulations, and standards.
Examples:
- ISO 27001
- SOC 2
- GDPR
- HIPAA
- NIST
- PCI DSS
GRC tools connect these pillars so risks are governed properly and compliance becomes proactive instead of reactive.
Why Are GRC Tools Important in 2026?
The business and regulatory environment in 2026 is more complex.
1. Regulatory Expansion
New privacy, cybersecurity, and AI governance laws continue to emerge globally. Organizations must now manage overlapping regulatory obligations across jurisdictions.
Cyber Risk Growth
Cyberattacks are more targeted, automated, and financially damaging. Regulators increasingly expect documented risk management and security controls, not just technical defenses.
3. Cloud and Third-Party Risk
Cloud-first strategies and vendor ecosystems introduce new exposure points. GRC platforms help track vendor security posture, access controls, and compliance gaps.
4. Audit Pressure and Reporting
Audits are no longer annual events. Continuous compliance and real-time reporting are becoming the standard, particularly in regulated industries.
How Do GRC Tools Work?
Modern GRC tools automate and streamline the entire risk and compliance lifecycle.
Risk Identification and Assessment
Modern GRC platforms automate core risk tasks, including risk registers, scoring models, likelihood/impact analysis, and identifying trends in risk data:
According to industry insights, GRC automation can significantly reduce manual effort, accelerate risk assessments, and provide real-time data visibility, enabling faster and more reliable decision-making.
Control Mapping to Regulations
Control mapping, where controls are linked once and reused across frameworks like ISO 27001, SOC 2, and GDPR is a major automation benefit of GRC software:
Some compliance platforms allow you to map controls once and apply them across multiple standards, reducing duplication of effort and enabling continuous compliance.
Compliance Tracking and Reporting
Dashboards with real-time compliance status, automated alerts, and centralized evidence are core automation features. GRC automation includes continuously monitoring compliance status and generating reports without manual effort, helping teams see where gaps exist ahead of audits.
Workflow Automation
Automated workflows assign tasks, collect evidence, and alert teams when thresholds are exceeded, eliminating manual handoffs:
Modern GRC tools automate workflows for tasks such as evidence collection, risk assessments, and compliance checks, which frees up teams to focus on strategic priorities rather than routine administrative work.
Workflow automation is a key driver of operational efficiency in GRC, reducing manual overhead and accelerating compliance processes.
What Are the Key Features of GRC Tools?
While platforms vary, leading GRC tools share common core capabilities:
Risk Registers and Scoring
Modern GRC tools centralize enterprise, IT, and cybersecurity risks in a single risk register, using customizable scoring models based on likelihood, impact, and business context.
For example, a global enterprise tracks cloud misconfigurations, ransomware exposure, and third-party access risks in one system. When a new threat emerges, risk scores update automatically, helping security leaders prioritize remediation before incidents escalate.
Policy and Control Management
GRC platforms streamline the creation, approval, versioning, and enforcement of policies and controls, ensuring teams always work from the latest approved documents.
For example, during a GDPR policy update, legal, security, and IT teams collaborate in one workflow. The system records approvals, maintains version history, and confirms employees have acknowledged the updated policy, eliminating email chains and compliance gaps.
Compliance Framework Mapping
Leading tools offer pre-built control mappings across frameworks like ISO 27001, SOC 2, GDPR, HIPAA, and NIST, allowing organizations to define controls once and reuse them everywhere.
For instance, a SaaS company pursuing both SOC 2 and ISO 27001 maps shared controls, such as access management and incident response, across both frameworks, cutting audit preparation time nearly in half.
Audit Management
End-to-end audit management features support audit planning, evidence collection, issue tracking, and remediation, all from a centralized workspace.
Instead of scrambling before an annual audit, a compliance team continuously uploads evidence throughout the year. When auditors request documentation, reports are generated instantly, reducing audit fatigue and last-minute stress.
Third-Party Risk Monitoring
GRC tools automate vendor onboarding, risk questionnaires, scoring, and continuous monitoring, helping organizations manage supply-chain and partner risk.
Before onboarding a new cloud vendor, procurement and security teams assess security posture, data handling practices, and regulatory alignment, flagging high-risk vendors early and avoiding downstream compliance issues.
Dashboards and Reporting
Customizable dashboards provide real-time visibility into risk exposure, compliance status, and audit readiness, tailored for executives, CISOs, and compliance leaders.
A CISO uses executive dashboards during board meetings to show current risk trends, compliance posture, and remediation progress, turning technical data into clear, decision-ready insights.
What Types of GRC Tools Exist?
Not all GRC platforms are the same. Different tools serve different needs.
| GRC Tool Type | What It Covers | Best For |
| Enterprise GRC Platforms | End-to-end governance, enterprise risk management (ERM), compliance, audit, and third-party risk in one system | Large enterprises and regulated industries |
| IT GRC Tools | IT controls, access governance, change management, and system-level risk | IT teams and organizations with complex IT environments |
| Cybersecurity GRC Tools | Cyber risk assessments, security frameworks, incident response controls, and threat-aligned risk tracking | Security teams and CISOs |
| Third-Party Risk Management Tools | Vendor onboarding, security questionnaires, risk scoring, and continuous vendor monitoring | Organizations with large vendor ecosystems |
| Compliance-Focused Tools | Certification tracking, evidence collection, and audit readiness for specific standards | Startups, SaaS, and cloud-first companies |
How Do GRC Tools Support Regulatory Compliance?
Modern GRC tools are transforming compliance from an episodic, point‑in‑time exercise into a continuous, automated practice that dramatically reduces manual work and audit stress across the enterprise. Instead of preparing for compliance once a quarter or once a year, organizations now monitor control effectiveness in real time and automatically collect evidence as part of everyday operations, a shift that improves both readiness and accuracy.
For example, continuous compliance monitoring features in leading GRC solutions scan configurations, access controls, and policy adherence on an ongoing basis and alert teams the moment a deviation occurs, eliminating the reactive “audit crunch” many organizations still face.
Automated evidence collection is another cornerstone of this continuous model. Rather than chasing down screenshots, logs, and stakeholder responses, modern platforms automatically gather and timestamp artifacts from across systems, linking them directly to the relevant control for auditors to review. This approach has been shown to deliver 70–80% time savings during audit preparation and dramatically reduce human error compared to manual evidence gathering.
In real terms, teams that once spent weeks preparing for an external audit now maintain audit‑ready evidence year‑round, with dashboards and real‑time reporting providing clear snapshots of compliance status whenever needed.
Centralized evidence repositories also support audit readiness by tracking control performance and evidence provenance across frameworks like SOC 2, ISO 27001, NIST, and HIPAA, making it far easier to produce accurate, regulator‑specific reports on demand.
Meanwhile, automated regulatory reporting consolidates data into shareable formats for executives and auditors alike, turning what once was a major effort into a few clicks.
What Are the Benefits of Using GRC Tools?
Implementing GRC tools is no longer optional for modern enterprises. Beyond compliance, GRC tools help organizations make smarter, data-driven decisions that reduce risk and enhance operational performance.
Key Benefits of Using GRC Tools:
- Reduced Compliance Risk: Identify and remediate gaps before they become penalties.
- Improved Risk Visibility: Centralized dashboards provide real-time insight across enterprise, IT, and cyber risks.
- Operational Efficiency: Automate workflows, evidence collection, and reporting.
- Consistent Governance: Standardize policies and controls across teams and locations.
- Better Executive Decision-Making: Data-driven insights guide strategy and prioritization.
- Audit Readiness: Continuous monitoring ensures teams are prepared year-round.
- Third-Party Risk Management: Track and manage vendor and supplier risks proactively.
What Are the Limitations or Challenges of GRC Tools?
While GRC platforms offer many benefits, organizations often encounter practical challenges when implementing them. These hurdles can affect adoption, ROI, and overall effectiveness if not addressed early.
Key Challenges of GRC Platforms:
- Implementation Complexity: Large deployments require careful planning, configuration, and stakeholder buy-in.
- Cost Considerations: Enterprise-level platforms can be expensive for smaller organizations or startups.
- Data Integration Challenges: Legacy systems and siloed data may complicate integration with the GRC tool.
- User Adoption Issues: Poor user experience or insufficient training can limit effectiveness and reduce ROI.
What Are the Top 10 GRC Tools in 2026?
The following tools were selected based on market adoption, feature depth, scalability, regulatory coverage, and integrations.
ServiceNow GRC
ServiceNow GRC is a powerful enterprise‑grade platform that unifies governance, risk, and compliance with ServiceNow’s broader IT Service Management and security operations ecosystem.
Its strength lies in seamless integration across IT workflows, risk processes, and incident management, enabling teams to automate risk assessments, policy lifecycles, and compliance tasks from a single interface.
Best for: Large enterprises with complex IT environments
RSA Archer
RSA Archer is a long‑standing, risk‑centric GRC platform renowned for its deep regulatory mapping and configurable risk frameworks that align audit, compliance, and enterprise risk functions.
By centralizing risk data and enabling cross‑domain insights, Archer empowers risk leaders to anticipate threats, enforce consistent controls, and streamline compliance reporting across the enterprise.
Best for: Risk-focused enterprises and regulated industries
MetricStream
MetricStream is a unified GRC platform that brings together enterprise risk management (ERM), compliance, audit management, and policy governance within a single framework, enabling organizations to break down risk silos and streamline oversight.
Its strengths lie in scalable architecture and robust framework support, making it well‑suited for large enterprises and global organizations’ regulatory compliance.
Best for: Global organizations managing multiple frameworks
LogicGate Risk Cloud
LogicGate Risk Cloud is a highly customizable, workflow‑driven GRC platform designed to adapt to unique risk and compliance processes without heavy coding or rigid templates.
Its strength lies in intuitive visual workflows and dynamic automation, allowing teams to model risk scenarios, automate approvals, and align controls with business context in real time.
Best for: Organizations needing tailored risk processes
OneTrust GRC
OneTrust GRC stands out for its strong alignment between privacy, risk, and compliance, making it a go‑to choice for organizations navigating complex data protection mandates like GDPR, CCPA, and emerging global privacy laws.
It brings together risk assessments, control mapping, and privacy program management with regulatory intelligence, helping teams operationalize compliance while maintaining a unified view of enterprise risk.
Best for: Privacy-first and data-driven businesses
IBM OpenPages
AIBM OpenPages is an enterprise‑scale GRC platform that leverages AI‑powered insights and advanced analytics to help organizations identify emerging risks and streamline governance across complex environments.
With strong support for risk quantification, regulatory frameworks, and cross‑domain workflows, it enables large organizations to break down silos and connect risk data with operational outcomes.
Best for: Large enterprises with advanced risk analytics needs
SAP GRC
SAP GRC is an ERP‑native governance, risk, and compliance platform tightly integrated with SAP’s broader business suite, providing organizations with seamless access control, financial compliance, and risk automation directly within their enterprise systems.
Its strength lies in enforcing segregation of duties (SoD), monitoring critical access paths, and aligning risk controls with core business processes, making it valuable for SAP‑centric enterprises.
Best for: SAP-centric organizations
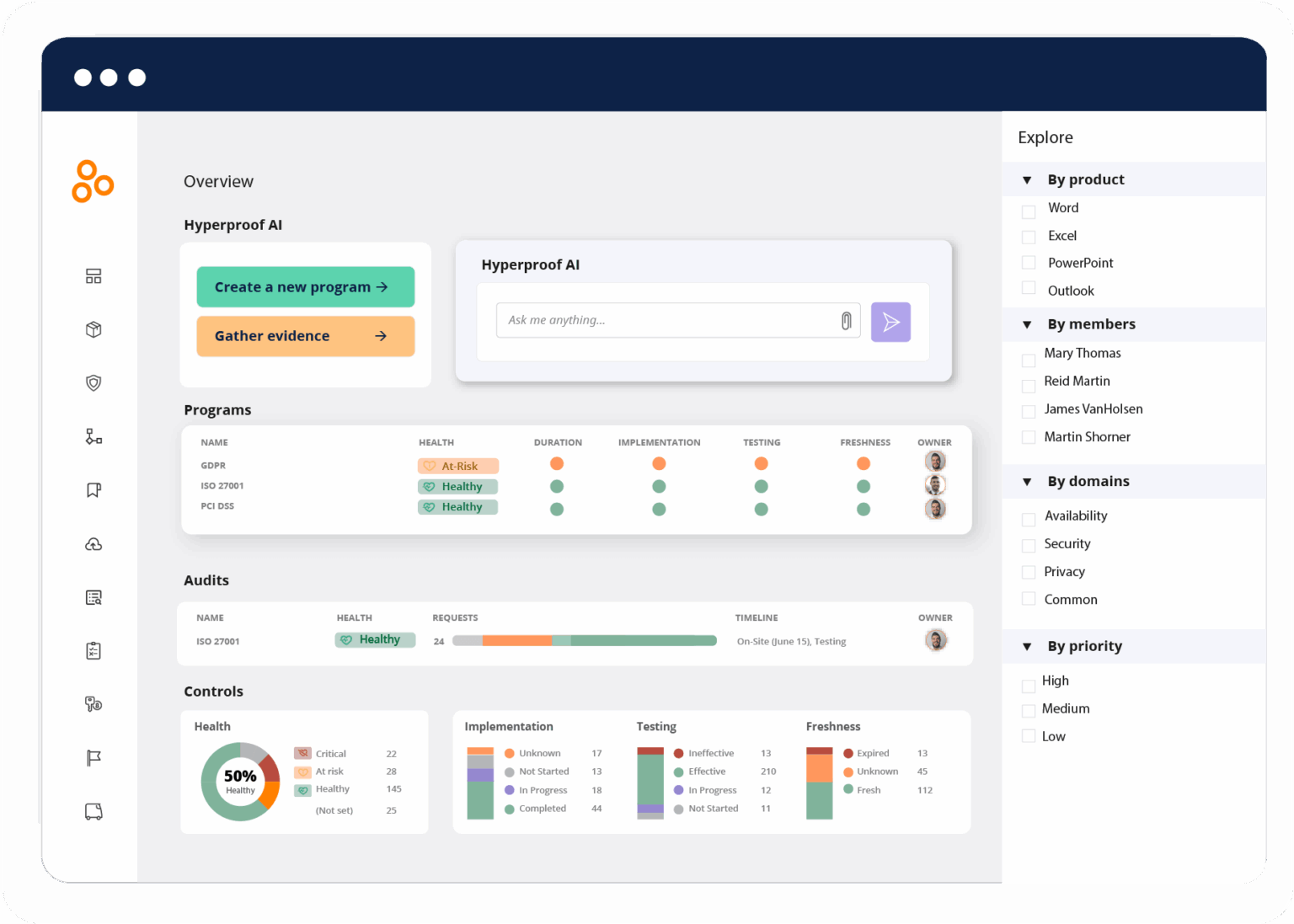
Hyperproof
Hyperproof is a compliance‑focused GRC platform built to automate evidence collection, streamline audit workflows, and keep teams continuously prepared for both internal and external assessments.
Its user‑friendly interface and purpose‑built automation help organizations reduce manual work, centralize documentation, and quickly demonstrate compliance with standards like SOC 2, ISO 27001, and HIPAA.
Best for: SaaS companies pursuing certifications
AuditBoard
AuditBoard is a GRC platform built around strong collaboration features that help audit, compliance, and risk teams work more effectively together throughout the entire risk lifecycle.
Its intuitive workflows simplify SOX testing, control evaluations, and issue tracking, while built‑in dashboards make it easy to monitor progress and keep stakeholders aligned.
Best for: Internal audit and SOX compliance
Drata
Drata is a cloud‑native compliance automation platform that continuously monitors security controls, system configurations, and evidence collection to help organizations maintain real‑time compliance with standards like SOC 2, ISO 27001, and GDPR.
Its automated workflows and integrations with modern cloud stacks reduce manual effort, accelerate audit readiness, and provide teams with up‑to‑date compliance posture visibility.
Best for: Startups and cloud-first organizations
How Should Organizations Choose the Right GRC Tool?
Selecting the right GRC platform requires more than feature comparison, it’s about alignment with your organization’s risk profile, compliance obligations, and operational needs.
Key Factors to Evaluate:
- Company Size and Industry: Ensure the platform fits your organizational scale and sector-specific needs.
- Regulatory Requirements: Check for built-in compliance support for relevant frameworks like GDPR, SOC 2, ISO 27001, or HIPAA.
- Integration with Existing Tools: Look for seamless connections to ERP, ITSM, security, and productivity systems.
- Scalability and Reporting Needs: Confirm the solution can grow with your business and deliver actionable dashboards and reports.
Who Should Use GRC Tools?
GRC tools are becoming indispensable across a broad spectrum of organizations, not just traditional risk and compliance teams, because they provide a unified way to manage risk, governance, and regulatory obligations at scale.
Enterprises of all sizes increasingly adopt GRC platforms to automate compliance and centralize risk visibility; in fact, more than 60% of organizations globally are now deploying GRC solutions to strengthen operational controls and reporting workflows.
Large, regulated industries such as financial services (BFSI) lead adoption due to stringent requirements around SOX, Basel III, AML, and real‑time risk monitoring, making automation essential for compliance accuracy and audit readiness.
Healthcare providers also rely heavily on GRC tools to meet HIPAA, GDPR, and clinical risk standards. Structured platforms help reduce compliance gaps and align clinical operations with regulatory frameworks, significantly improving compliance outcomes.
SaaS and cloud‑first organizations find GRC solutions particularly valuable for managing continuous compliance across SOC 2, ISO 27001, and privacy standards, with many teams reporting faster readiness for security audits and better alignment with customer procurement requirements.
Finally, even mid‑sized enterprises and SMEs are accelerating adoption, cloud‑native GRC deployments now make scalable, automated risk and compliance management accessible beyond large corporations, highlighting GRC’s role as a cornerstone of modern enterprise governance.
What Is the Future of GRC Tools Beyond 2026?
The future of GRC is rapidly shifting from periodic, manual compliance toward intelligent, automated, and security‑driven systems that continuously protect and enable the business. Industry analysts and technology leaders agree that traditional GRC approaches, characterized by spreadsheets, point‑in‑time audits, and siloed teams, are no longer effective in today’s dynamic risk landscape.
Instead, the next generation of GRC tools will be powered by AI, predictive analytics, continuous monitoring, and deep integration across risk domains.
AI is already reshaping GRC operations by enabling real‑time risk scoring and predictive insights that go far beyond reactive reporting. According to IBM’s recent analysis, AI‑driven GRC platforms can automatically update risk registers, detect control failures in real time, and apply predictive models that flag emerging threats before they materialize. This turns GRC from a backward‑looking compliance exercise into proactive risk management.
Experts also emphasize the rise of continuous compliance and control monitoring. Rather than waiting for quarterly audits, AI‑enabled models continuously assess controls, sending alerts and remediation tasks as issues occur. Analyst coverage on emerging GRC trends predicts that continuous control monitoring powered by machine learning will be mainstream by 2026, vastly reducing audit cycles and enhancing regulatory alignment.
Beyond risk and compliance automation, industry thought leaders highlight a broader convergence of cybersecurity, risk, and compliance.
Modern platforms are extending their scope to integrate with threat intelligence, identity systems, and security operations, creating a unified Cyber GRC layer that aligns risk governance with actual security events. This integration closes the feedback loop between security breaches and compliance reporting, enabling teams to respond faster and more strategically.
Experts also note that AI will reframe the role of GRC professionals rather than replace them. Conversations among practitioners, for example, on forums like Reddit, reflect a consensus that while AI can automate evidence collection, control mapping, and routine reporting, human judgment remains essential for interpreting risk context, prioritizing remediation, and communicating insights to executives and auditors.
Frequently Asked Questions
They help organizations manage governance, risk, and regulatory compliance from one platform.
No, many modern tools are designed for startups and mid-sized businesses.
Compliance tools focus on regulations, while GRC tools cover governance and risk holistically.
Yes, many platforms include cyber and IT risk management features.
Most leading tools support ISO, SOC, GDPR, HIPAA, NIST, and more.
Forward Thought
In 2026, GRC is no longer just a compliance task, but a strategic advantage. Modern GRC tools centralize risk, automate compliance, and provide real-time insights, helping organizations stay audit-ready while reducing manual effort.
By choosing the right platform, enterprises, SaaS companies, and regulated organizations can proactively manage risk, ensure continuous compliance, and strengthen governance.
With AI-driven risk scoring, automated audits, and cyber GRC convergence on the horizon, adopting a modern GRC solution is important for resilience, efficiency, and better decision-making.





