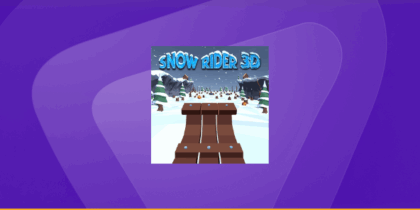
You’ve probably seen the latest buzz in the AI world, an open-source agent that doesn’t just chat but acts: automating tasks, managing calendar invites, running scripts and even sending messages on your behalf. That’s Clawdbot! A tool that’s been viral across the tech community and social media.
But as with anything powerful, the upside comes with serious security concerns. In this guide, we’ll break down how Clawdbot works, what makes it unique, why it’s sparking worry among security pros, and what users are saying online, so you can decide whether it’s right for your system.
What Is Clawdbot?
Clawdbot (recently renamed Moltbot due to trademark issues) is an open-source, locally-running AI agent. Unlike cloud-hosted assistants like Siri or Alexa, Clawdbot lives on your machine or server, connecting large language models (like Claude or GPT) to real-world actions, such as:
- Executing shell commands on your computer
- Automating messaging (WhatsApp, Telegram, Slack, Discord)
- Reading and summarizing emails or files
- Scheduling events
- Running scripts or custom automation workflows
It’s a fully autonomous digital assistant that does things instead of just answering questions.
Why Is Clawdbot Gaining Attention?
Clawdbot’s popularity exploded because it lets you:
- Run the AI locally, meaning no cloud dependency.
- Integrate tightly with messaging platforms.
- Customize it with community-built skills.
- Run it on spare hardware (like a Mac Mini) for 24/7 uptime.
Some enthusiasts are even buying hardware specifically to host it.
Who Should and Shouldn’t Use Clawdbot?
Clawdbot isn’t a one-size-fits-all tool. While it offers impressive automation potential, it also demands a level of technical awareness that not every user has or needs.
Who Clawdbot Is Best For
Clawdbot makes the most sense for developers, automation engineers, and researchers who already work with scripts, APIs, and system-level tools. If you’re comfortable managing virtual machines, containers, and access permissions, you’ll be better equipped to isolate the bot, monitor its activity, and respond quickly if something goes wrong.
These users often understand how to test experimental software safely and are more likely to treat Clawdbot as a controlled environment rather than a plug-and-play assistant.
Who Should Avoid Using Clawdbot
On the contrary, casual users looking for a simple AI helper should probably steer clear. Running Clawdbot on a work computer or a personal machine that stores sensitive data, such as passwords, private keys, or business documents increases risk.
If you’re not comfortable troubleshooting network settings, managing permissions, or recognizing suspicious behavior, Clawdbot may introduce more problems than benefits.
How Does Clawdbot Work?
At its core, Clawdbot is a gateway that connects an LLM to your machine and messaging systems. When you install and configure it:
- The agent runs a local server (often on port 18789).
- It integrates with your chat platform (via tokens/API keys).
- It executes actions using your system permissions, meaning if you grant it power, it can execute commands like any local program.
This architecture enables automation, but it also expands the attack surface dramatically, because it’s no longer just a chat engine; it’s a tool with hands in your system.
Is Clawdbot a Security Risk?
Here’s where things get serious. Security experts have flagged several major risks inherent to Clawdbot’s design and deployment:
1. Prompt Injection Vulnerabilities
Clawdbot reads and interprets text from emails, messages, documents, and even web content. Because it treats these inputs as instructions, attackers can craft malicious content that tricks the AI into executing harmful commands, a threat called prompt injection.
Experts warn this problem is not fully solved and will remain a risk until more robust sandboxing or safety layers are widely adopted.
2. Exposure of API Keys & Credentials
Multiple security analyses revealed that hundreds of Clawdbot gateways are exposed online without authentication, meaning anyone could access:
- Private chat logs
- API credentials
- Bot tokens
- OAuth secrets
In some cases, researchers could even achieve remote code execution, which would let attackers take control of the host system.
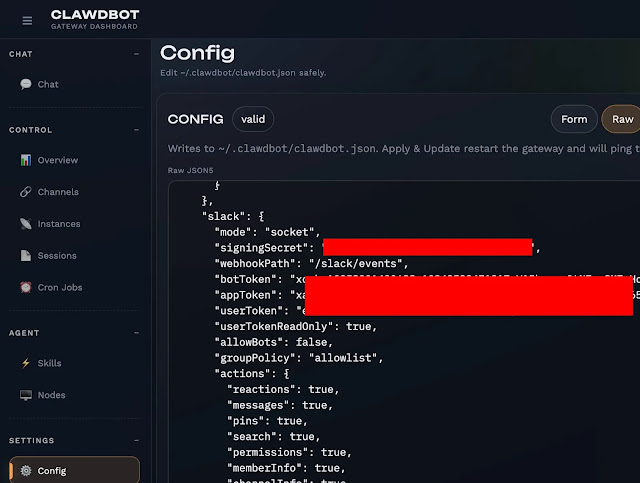
3. Full System Access Means Full Blast Radius
Unlike typical apps, Clawdbot can:
- Read and write files
- Send messages and web requests
- Execute arbitrary commands
- Interact with browsers and network services
If left unchecked, these permissions could lead to forgotten credentials being stolen or harmful actions executed without user consent.
What Do People Think About Clawdbot’s Security?
Here’s what people are saying, unfiltered voices from developers and experimenters:
“Running it on a VM is best practice, but prompt injections are still not out of the question.”
— User on r/aiagents
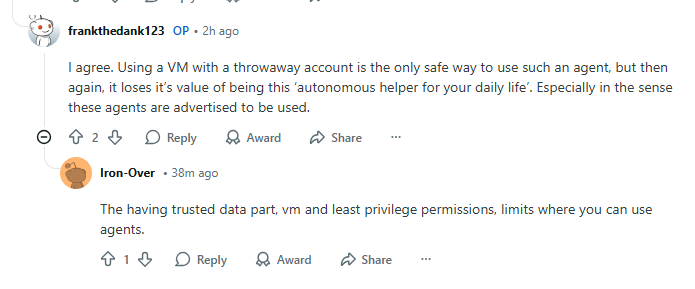
“Full configuration dumps with API keys and conversation histories … no authentication required.”
— User on r/ClaudeAI

Some users appreciate its automation capabilities but still face security concerns: “Security breaches and worth buying a Mac Mini? Probably run on spare hardware first.” — User on r/productivity
How to Reduce Risk If You Still Want to Use Clawdbot
Clawdbot can be incredibly powerful, but power without guardrails is where things get risky. If you’re curious about experimenting with it, or already planning to, there are several steps you can take to minimize damage.
- First, never run Clawdbot directly on your primary system. Treat it like an experiment, not a daily-driver app. The safest approach is to run it inside a virtual machine (VM), container, or separate device. This way, if something goes wrong, your main files and credentials remain untouched.
- Next, always use separate API keys specifically created for Clawdbot. Avoid reusing keys tied to production services or personal accounts. If a key is ever exposed, you can revoke it instantly without impacting anything else.
- Network isolation is another smart move. Limit what Clawdbot can access on your local network and restrict outbound connections where possible. This reduces the chances of data being silently sent to unintended destinations.
- Where supported, apply read-only permissions. If Clawdbot only needs to read files, don’t allow it to modify or delete them. Less access means less harm.
- Finally, keep an eye on outbound traffic and activity logs. Monitoring what Clawdbot is doing in the background can help you spot unusual behavior early, before it becomes a real problem.
Used carefully, Clawdbot can be explored safely. The key is treating it as a powerful tool that deserves strict boundaries, not blind trust.
Clawdbot vs Traditional AI Assistants: What’s the Real Difference?
| Feature | Clawdbot | Traditional AI Assistants (ChatGPT, Browser AI Tools) |
| Primary Function | Executes real actions on your system | Answers questions and generates content only |
| System Access | Can read, write, and execute commands locally | No direct access to your files or operating system |
| Where It Runs | Locally on your machine or server | Cloud-based and sandboxed |
| Permission Scope | Depends on what the user grants — often broad | Extremely limited and controlled |
| Automation Capability | High — can automate scripts, messages, and workflows | Low — mostly manual copy-and-paste actions |
| Risk Level | Higher due to system-level access | Lower due to isolation from your device |
| Prompt Injection Impact | Can trigger real system actions | Usually limited to misleading responses |
| Best Use Case | Advanced users building automation pipelines | Everyday users seeking information or writing help |
Frequently Asked Questions
Not recommended. Security pros advise running it in a sandboxed environment, VPS, or virtual machine instead of your primary PC.
Yes, if you grant it access, and it’s tricked via prompt injection. That’s why isolation is critical.
You can, but only if you’re comfortable with networking, containerization, and security best practices, otherwise wait for safer, consumer-oriented builds.
It can transmit data to the LLM provider you connect (OpenAI, Claude, etc.), so privacy considerations depend on that configuration.
In most cases, Clawdbot itself isn’t flagged as malware because it’s a legitimate open-source tool. However, its behavior, such as executing scripts or making network requests, may trigger alerts depending on your security software.
Only if it’s granted permission or runs on a system where those files are accessible. Clawdbot doesn’t automatically steal data, but broad system access increases the risk if something goes wrong. This is why separating environments and limiting permissions is critical.
So far, there are no confirmed large-scale attacks directly attributed to Clawdbot. But, researchers have already discovered publicly exposed instances and unsecured dashboards. These findings suggest the risk is more about misconfiguration and misuse than the tool itself.
Wrap Up
Clawdbot represents an exciting leap in agent-based AI, a tool that does things, not just talks. But that power is a risk too. While early adopters celebrate its automation potential, security professionals are raising red flags about, prompt injection, credential leaks, exposed control panels, and full system access
If you’re considering trying it, do so with extreme caution, isolate it in a safe environment and understand the risks before giving it control of your systems.