Table of Contents
Have you ever heard the story of Little Red Riding Hood? I believe you might have.
The story is about a young girl who leaves her house and treks into the woods to meet her ailing grandma. However, little did she know that her grandma was already locked up in the cupboard, and the one disguising as her was the big bad wolf. The wolf wanted to eat the young girl and the food she had in her basket.
Hackers can sometimes be like that, the big bad wolf, strolling in the woods (the Internet) and seeking unsuspecting Internet users. They can disguise as a trusted someone or a source and do what they are good at (i.e., stealing), without leaving a hint.
IP address spoofing is one such practice that hackers, spammers, or scammers use to con you or rip you off your sensitive information.
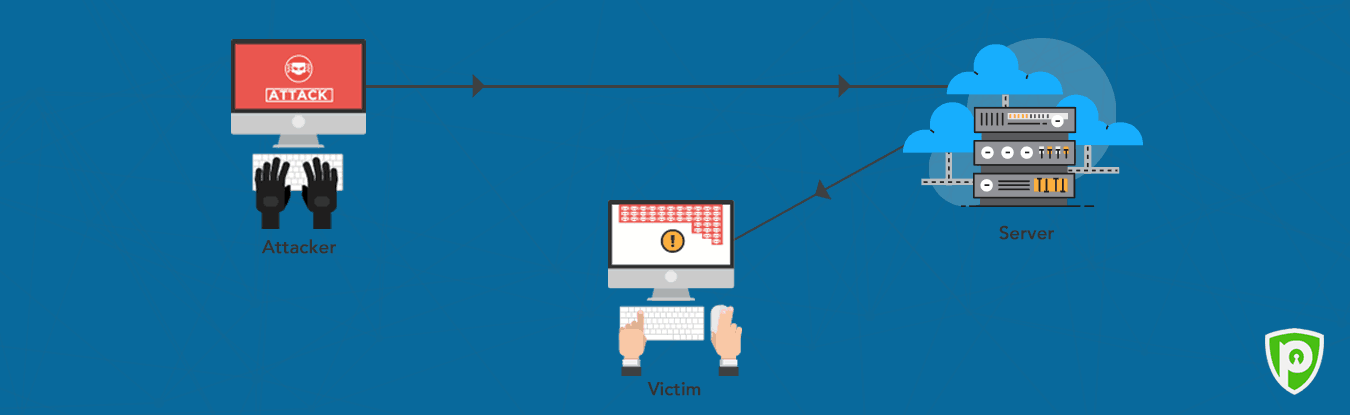
What is IP spoofing?
IP spoofing is a technique in which the attacker creates an IP with a fake or bogus source IP address in its header. The IP is spoofed with fake information to either hide the sender’s identity or help him launch sneaky attacks like DDoS.
What is IP spoofing used for?
Although IP address spoofing is a tough nut to crack for average Internet users, having a basic understanding about it would allow many to keep their data safe from future IP address spoofing attacks.
Hackers use the notorious technique for several nefarious reasons. For instance, an attacker would never want to get caught doing cybercrimes like spamming or scamming. As a result, the attacker would spoof the IP to keep suspicious eyes away from him.
Moreover, the technique can orchestrate major attacks like DDoS to target specific systems or infrastructures as explained above.
Marek Majkowski gave a detailed overview of a spoof-based attack during a DEFCON event, Packet Hacking Village 2017. While discussing direct attacks, Marek explained that a direct attack occurs, “when the attacker just transmits packets directly to us, directly to the target, without any amplification and a reflection in the middle. It’s just packets from the source, the targets, that’s it. “But we cannot trace that attacker because the source IPs are spoofed, so we don’t know who actually originated them,” he further explained.
That said, did you know that an average DDoS attack can cost companies over $2.5 million?
Is IP spoofing illegal?
Spoofing isn’t illegal by itself because you may need to fake your IP address to hide your Internet activities and thus enjoy online privacy. However, if someone uses spoofing to pretend to be someone else and, as a result, indulges in criminal acts such as identity theft, then it is patently illegal.
IP spoofing-related incidents
The IP address spoofing technique has aided cybercriminals in causing a great number of attacks. These attacks include Blind Spoofing, Non-Blind Spoofing, Man-in-the-middle attacks, and the notorious Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack.
- In a survey conducted by the experts at the University of California San Diego, it was found that almost one-third of the Internet was subject to DDoS attacks from March 2015 to February 2017.
In the research, the experts highlighted two major types of denial-of-service attacks: Direct and Reflection attacks.
- In 2017, the Wall Street Journal reported that personnel of North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) experienced hacking attempts made on their phones. The members of the forces were deployed near the Russian border, and they claimed that someone attempted to gain access to their iPhone but failed due to an added security layer.
Although the attack seemed to be carried out from Moscow, but the IP or location could have been spoofed to mislead the experts.
- In late 2016, Incapsula (a cloud-based application delivery platform) experienced a major DDoS attack which was later termed as LEET. The attack was targeted at anycast IPs of the CDN.
The massive Distributed Denial of Service attack first hit a major 400 Gbps mark and later peaked at 650 Gbps. Like other DDoS attacks, the attacker couldn’t be pinpointed due to IP spoofing which allowed him to mask the source location.
The current state of IP spoofing
Now that we have learned what IP Spoofing is and how it has contributed to several major attacks, let’s take a quick look at its current state.
The Spoofer project, operated by CAIDA and funded by the US Department of Homeland Security Science and Technology Directorate, can give us a detailed insight into the current state of IP address spoofing around the globe.
The project aims to understand how IP address spoofing allows cybercriminals to exploit the Internet.
In the following image, you can see the different locations from where the participants ran the test.

The next image shows the regions that are more vulnerable to attacks caused by IP spoofing.

Another insightful chart that shows how many IPs tested during a certain period were spoofable.

How IP spoofing works
The Internet Protocol, or IP, is used for sending data over a network or the Internet. Since the data is transmitted over the Internet in packets, the IP packets come with a Header that contains different information.

Image Credit: Incapsula.com
The source IP address tells the endpoint where the data came from. So, when an IP spoofing attack occurs, the source IP address is masked with a fake or bogus IP address.
How to prevent IP spoofing?
Spoofing attacks can be sneaky and difficult for an average Internet user to detect. However, users can take some measures to prevent spoof-based attacks.
- If you don’t want to get your hands dirty, it is best to use a reliable Internet Service Provider (ISP). A good ISP uses state-of-the-art infrastructure to not only provide a good Internet connection but also mitigate or prevent Internet attacks.
- Secondly, you may want to configure packet filtering on your router to keep malicious or fake IP packets from routing through your network. Through Ingress and Egress filtering you can filter all the inbound or outbound traffic on your router. Go to your router’s official website’s help page to learn how to set packet filtering.
- To encrypt the packets, you may also use web encryption protocols like Transport Layer Security (TLS) or HTTPS. Consequently, an attacker might be able to access the network, but he won’t be able to modify or change the packets due to encryption.
- If you suspect a spoofer on your network, you can use spoofing detection tools to stop the attack before it compromises your private information.
How PureVPN can help you protect against IP Spoofing attacks
IP address spoofing requires the attacker to be on your network. More importantly, the attack needs some ideal conditions for execution. For instance, packets must be unencrypted to execute an IP spoofing attack.
Here, a VPN such as PureVPN is your best bet. Its military-grade encryption can help you stay safe from spoof attacks.
When you connect to a VPN, your data is transmitted through an encrypted tunnel to the ISP. Everything that goes through the tunnel is protected with 256-bit encryption.

So, even if an attacker plans to spoof your IP packets, he won’t be able to do it without resolving the packets, which is impossible due to end-to-end encryption.
IP spoofing FAQs
The following are answers to some of the most frequently asked questions about IP spoofing:
What is spoofing used for?
Spoofing is a method commonly used by hackers and snoopers to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information or execute major cyber-attacks, such as DDoS.
How would you detect IP spoofing?
Bogon filtering, ingress filtering, egress filtering, and packet filtering are effective ways to detect spoofed IP packets and remove them with minimal collateral damage.
What is a good IP spoofing example?
A distributed-denial-of-service attacker often uses IP spoofing to overwhelm devices and networks with malformed packets that appear from a legitimate source.
What are some IP spoofing tools?
IP spoofing poses a major online threat to individuals and businesses today due to the widespread availability of automated spoofing tools like AntiDetect and FraudFox.
What is anti-spoofing?
To put it simply, anti-spoofing is a method for detecting and rejecting packets with a spoofed source address.
What does spoof ip adress mean?
Spoof ip adress refers to masking or changing your real IP address to appear as if you are browsing from a different location for privacy or security reasons.
Is it safe to spoof ip adress?
Spoof ip adress can improve privacy when done through trusted VPNs or proxy services, but misuse may violate website terms of service.









How does one detect Ip spoofing? What aresome IP spoofing detection techniques?
You can use the Bogon Filters method, MAC Limiting, TTL Analysis or Route Checking.
Thank you for this article. Our router has been completely hijacked. I suspect my neighbor. I will try some of your pointers.