Password managers are essential today! With hundreds of online accounts per person, using a password manager to generate, store, and autofill unique credentials is one of the easiest ways to lock down your digital life.
Yet not all solutions are created equal… and LastPass has become a controversial name. In this blog, we’ll explore what makes a password manager secure, LastPass’s security and privacy record, recent breaches and phishing threats, and more.
Why Password Managers Matter?
Remembering dozens or hundreds of strong, unique passwords just isn’t realistic. That’s why a reliable password manager is important to use. But how do they actually keep you safe?
Here’s how:
- Zero-knowledge encryption — Your master password is yours alone. It never leaves your device, and your vault gets encrypted before it’s stored in the cloud. Even the provider can’t see what’s inside.
- Strong encryption standards — Most reputable services use AES-256 encryption, the same level trusted by banks and governments. That means your data is locked down with serious cryptographic muscle.
- Two-factor authentication (2FA) — This adds a second security checkpoint, like a one-time code or hardware key, so even if someone guesses your master password, they still can’t get in.
- Secure autofill — A good password manager won’t blindly fill credentials everywhere. It checks website domains carefully to help prevent phishing attacks.
- Breach monitoring — If one of your saved accounts shows up in a known data leak, you’ll get alerted so you can act fast.
When a password manager consistently delivers on all of these fronts, it’s generally a strong contender. That said, even well-designed systems can run into problems, and that’s where reputation, transparency, and track record start to matter just as much as features.
LastPass: Features and Security Claims
LastPass has long been one of the most recognizable password managers worldwide with:
- A long list of features: vault sharing, secure notes, password audits, breach alerts, cross-device sync.
- Zero-knowledge architecture, meaning LastPass can’t access your master password or unencrypted vault content.
- AES-256 encryption with salted hashes and PBKDF2 key strengthening.
- External auditing and a bug bounty program.
These are all signs of strong underlying security, on paper. But in practice, implementation and real-world breaches matter just as much.
LastPass Data Breaches & Security Incidents
One of the biggest questions around LastPass is simple: Has it been breached?
Yes, and multiple times.
1. The 2022 Vault Breach
In late 2022, an attacker stole:
- A copy of the customer database
- Some copies of encrypted user vaults
- Some unencrypted metadata
The stolen encrypted vaults weren’t immediately decryptable, but weak master passwords could be cracked offline over time.
2. ICO Fine in 2025
In late 2025, the UK’s Information Commissioner’s Office fined LastPass £1.2 million for failing to implement robust technical and security measures during that breach, exposing 1.6 million UK users’ data.
3. Ongoing Phishing Attacks in 2026
As recently as January 2026, LastPass warned about widespread phishing campaigns trying to trick users into divulging their master passwords via fake “maintenance” emails.
And prior campaigns have impersonated LastPass via fake death certificate notices to harvest credentials.

What LastPass Breach Means for Your Security?
Here’s the honest, balanced takeaway from LastPass’s security journey, and why opinions are still divided. On one hand, the foundation is strong. LastPass was built on solid security principles:
- Zero-knowledge encryption — meaning your master password isn’t stored or known by the company.
- AES-256 encryption — the same encryption standard used by financial institutions and government systems.
- 2FA and hardware key support — including options like authenticator apps and physical security keys.
- Independent security audits and a public bug bounty program — which signal transparency and ongoing testing.
From a technical architecture standpoint, these are exactly the features security professionals look for in a password manager. But real-world incidents changed the conversation. During the 2022 breach, attackers gained access to encrypted vault backups and customer metadata. Even though vaults were encrypted, they were taken.
Because attackers had offline copies of vaults, users with weak master passwords faced a theoretical risk of brute-force cracking over time. Communication around the breach was widely criticized for being slow and evolving in stages, which impacted user trust.
So what does this actually mean?
It means the cryptography itself wasn’t broken. AES-256 wasn’t cracked. Zero-knowledge wasn’t reversed. Instead, the issue was operational security and infrastructure weaknesses that allowed attackers to access stored vault data in the first place.
So, the blueprint was strong. The execution faltered. And in cybersecurity, trust isn’t just about encryption algorithms; it’s about how a company manages risk, responds to incidents, and communicates when something goes wrong.
That’s ultimately why LastPass remains technically capable, yet more controversial today than it was before 2022.
What Did People Experience About LastPass?
User sentiment around LastPass today is polarized. Some users stick with it, and many long-time users appreciate:
- Easy autofill and cross-platform syncing.
- Broad feature set and familiarity.
- Dark web monitoring and password strength tools.
Many users have left or warned others. Online forums and review platforms show:
- 80% of Trustpilot reviews are 1 star; users complain about lost access, billing issues, and poor support.
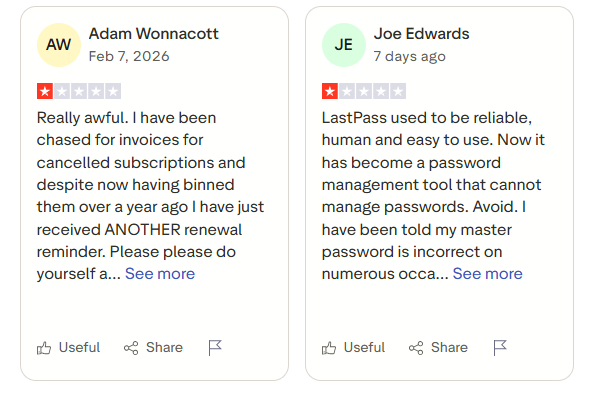
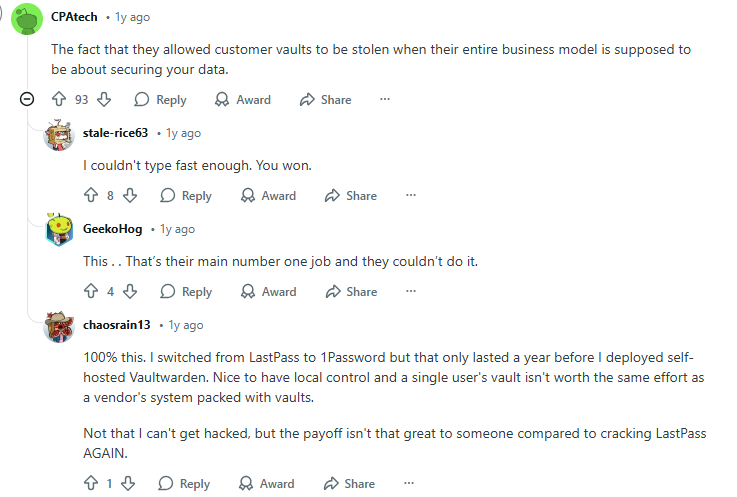
- Some users report switching to alternatives because of security concerns.
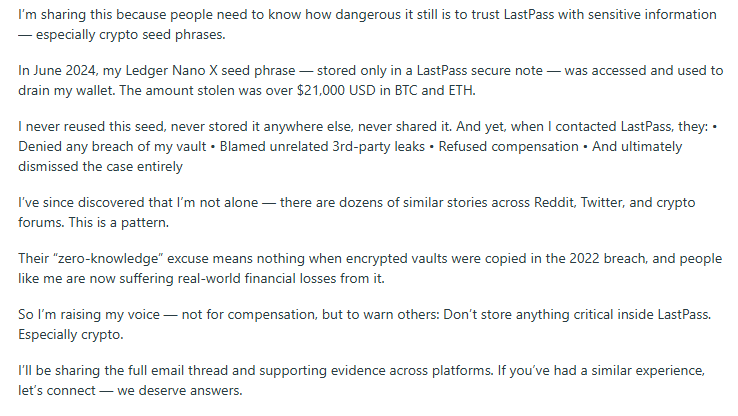
- Stories of cryptocurrency loss (from seed phrases stored in LastPass notes) are shared in some communities.
How Does Switching to PureVPN Password Manager Keep You Secure
PureVPN Password Manager is relatively new compared to legacy services like LastPass, but has a strong backup of PureVPN long built reputation to provide:
- Zero-knowledge encryption – Only you can access your vault.
- Cross-device sync – Access passwords on desktop, mobile, and browser.
- Secure password generation – Creates strong, unique passwords effortlessly.
- Autofill & secure login – Automatically fills credentials only on verified sites.
- Breach alerts – Notifies if any saved accounts appear in known leaks.
- Simple vault organization – Store passwords, notes, and credentials in one place.
- Two-factor authentication (2FA) – Adds an extra layer of protection.
Wrap-Up
Passwords are one of the weakest links in digital security, and a good password manager is essential to reduce your risk. LastPass still ticks many of the right boxes, but past breaches and user trust issues make it a less clear winner than it once was. You must prioritise your password privacy without thinking much!
Frequently Asked Questions
It uses strong encryption but has a mixed security history, including major breaches. Continued phishing attacks also highlight ongoing risks.
That depends on your risk tolerance. But switching to a trusted service that has a history of providing total privacy is a wise decision.
Yes, with strong encryption and zero-knowledge design, they’re safer than reusing passwords.








