Cybersecurity threats have evolved into highly automated, fast-moving operations that can overwhelm even the most mature security teams. At the same time, organizations are generating more security data in cloud workloads and SaaS platforms to endpoints, networks, and third-party integrations. Relying on manual processes to keep up with this volume is no longer realistic.
This is where SecOps automation plays a critical role. SecOps automation enables security teams to automate repetitive, time-consuming, and high-volume tasks across the Security Operations Center (SOC). Instead of reacting manually to every alert, analysts can focus on real threats, strategic risk reduction, and continuous improvement of security posture.
This guide provides a deep, end-to-end explanation of SecOps automation, what it is, how it works, why it matters, and how organizations are applying it in real-world security operations today.
What Is SecOps Automation?
SecOps automation is the use of automated tools and workflows to handle routine security tasks like threat detection, alert analysis, and incident response. It integrates directly with security systems such as SIEM, SOAR, and endpoint protection tools.
Instead of relying on manual investigation, automation processes alerts and triggers responses automatically. This reduces response time and minimizes human error in security operations.
SecOps automation builds on traditional SecOps by replacing repetitive manual work with scalable workflows. As threats grow faster and more complex, it helps security teams stay efficient and in control.
Understanding SecOps in Modern Security Operations
Security Operations (SecOps) refers to the operational side of cybersecurity responsible for continuously monitoring systems, identifying threats, investigating suspicious activity, and responding to incidents.
SecOps teams operate primarily within a Security Operations Center (SOC), where security analysts manage alerts and incidents around the clock.
Historically, SecOps relied heavily on:
- Manual log analysis
- Static correlation rules
- Ticket-based workflows
- Human-driven investigations
While effective in smaller environments, this approach breaks down under modern threat volumes.
The Role of SecOps Teams in Enterprises
In today’s enterprises, SecOps teams are expected to:
- Monitor logs and alerts from SIEM platforms
- Detect intrusions, malware, and insider threats
- Investigate suspicious behavior across endpoints and cloud workloads
- Execute incident response and containment
- Manage vulnerabilities and remediation workflows
- Support compliance, auditing, and reporting
As businesses expand their digital footprint, the operational burden on SecOps teams grows exponentially.
SecOps vs DevOps vs DevSecOps
Understanding how SecOps fits alongside other operational models helps clarify its role:
- DevOps focuses on speed, collaboration, and reliability between development and IT operations
- DevSecOps embeds security into the software development lifecycle
- SecOps focuses on protecting live production environments through monitoring and response
SecOps automation complements DevSecOps by ensuring that once applications and infrastructure are deployed, security enforcement and response can scale automatically.

Why Manual Security Operations No Longer Scale?
Manual security operations struggle because:
- Alert volumes are too high
- False positives consume analyst time
- Threats move faster than human response
- Cloud and hybrid environments increase complexity
- Skilled security talent is limited
These challenges make SecOps automation a necessity rather than an optimization.\
What Is SecOps Automation? (Detailed Explanation)
SecOps automation is the use of technology-driven workflows, integrations, and playbooks to automatically execute security operations tasks with minimal human intervention. It transforms security operations from reactive, manual processes into scalable, repeatable systems.
At its core, SecOps automation aims to:
- Reduce response time
- Improve detection accuracy
- Minimize human error
- Increase SOC efficiency
How SecOps Automation Integrates into Security Operations
SecOps automation does not replace existing tools. Instead, it connects them.
It integrates with:
- SIEM systems for log aggregation
- SOAR platforms for orchestration
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) tools
- Threat intelligence feeds
- Vulnerability management platforms
- Cloud security services
This integration allows security operations automation to work across the entire environment.
Automating Repetitive Security Tasks
Some of the most common tasks automated through SecOps automation include:
- Alert enrichment and triage
- IP, domain, and URL reputation checks
- Malware analysis
- Ticket creation and escalation
- Endpoint isolation and containment
- User account suspension
By automating these actions, SecOps workflow automation frees analysts to focus on complex investigations.
SecOps Automation, SIEM, and SOAR Explained
Modern security operations rely on multiple technologies working together, which often causes confusion between SIEM, SOAR, and SecOps automation. While these terms are closely related, they serve different purpose. Understanding how they fit together is essential for building effective, automated security operations.
| SIEM | SOAR | SecOps Automation | |
| Primary Purpose | Centralized visibility and monitoring | Automated incident response and orchestration | End-to-end strategy for automating security operations |
| Core Function | Collects, normalizes, and correlates logs | Executes automated response workflows | Connects people, processes, and tools |
| Focus Area | Threat detection and alerting | Incident response and remediation | Detection, response, and operational efficiency |
| Automation Level | Limited (mainly correlation rules) | High (playbooks and workflows) | Strategic automation across the SOC |
| Role in SOC | Provides context and alerts | Reduces manual response effort | Defines how automation is applied |
| Relationship | Feeds data into SOAR | Acts on SIEM alerts | Aligns SIEM and SOAR with SecOps processes |
Enhancing Detection, Response, and Remediation
With SecOps automation, organizations dramatically improve the speed and effectiveness of incident handling. Automated detection systems correlate telemetry from logs, endpoints, and network activity at machine speed, helping SOCs achieve significantly faster Mean Time to Detect (MTTD) and Mean Time to Respond (MTTR) compared with manual approaches.
Research shows automation can reduce MTTD and MTTR by more than 30% in many environments by eliminating manual triage bottlenecks and enabling real‑time alert processing.
Automation also standardizes incident response using predefined playbooks that execute coordinated actions, such as isolating compromised hosts and enriching alerts, consistently and without delay. In some enterprise studies, AI‑enabled automation has even cut MTTD and MTTR by over 75%, while reducing the volume of alerts needing human review by nearly 90%.
Because remediation occurs immediately when criteria are met, threats are contained faster and breach impact is significantly reduced. In practice, this shift turns lengthy, manual investigation cycles into real‑time containment workflows, allowing security teams to stay ahead of evolving threats rather than constantly playing catch‑up.
Why SecOps Automation Is Important
SecOps automation is critical as modern security teams face more threats, alerts, and complexity than manual processes can handle.
The Expanding Attack Surface
Cloud adoption, remote work, SaaS usage, and third-party integrations have dramatically expanded the attack surface. Manual monitoring simply cannot keep pace with the scale of modern environments.
Alert Fatigue and Analyst Burnout
SOC analysts routinely face thousands of alerts per day. Many are false positives, leading to alert fatigue, missed threats, and burnout. SecOps automation filters noise and prioritizes what truly matters.
Faster MTTD and MTTR
Automated security operations significantly reduce:
- Mean Time to Detect (MTTD)
- Mean Time to Respond (MTTR)
This directly reduces the cost and severity of security incidents.
Consistent Security Enforcement
Automation ensures policies are applied uniformly across systems, reducing errors caused by manual handling.
How SecOps Automation Works
SecOps automation works by connecting security tools, data sources, and response workflows into a unified system. It continuously collects and analyzes security data to detect threats in real time. Once an incident is identified, automated workflows trigger consistent response and remediation actions with minimal manual intervention.
Data Collection and Ingestion
SecOps automation begins with ingesting data from:
- Network devices
- Endpoints
- Applications
- Cloud workloads
- Identity systems
This data feeds into centralized log management and SIEM platforms.
Integration with SIEM Platforms
SIEM tools correlate events across systems, forming the foundation for threat detection automation. Automated correlation reduces manual investigation time.
Threat Detection and Analysis
Automation enables:
- Correlation of security events
- Threat intelligence enrichment
- Mapping activity to the MITRE ATT&CK framework
- Behavior analytics that detect anomalies
Behavior-based detection complements rule-based systems by identifying unknown threats.
Automated Incident Response
Using predefined playbooks, SecOps automation can:
- Block malicious IPs and domains
- Disable compromised user accounts
- Isolate endpoints via EDR
- Trigger notifications and tickets
Human-in-the-loop controls ensure oversight for high-risk actions.
- Reporting and Compliance Automation
SecOps automation supports:
- Automated audit trails
- Continuous compliance checks
- Security posture reporting
- Stakeholder dashboards
This simplifies compliance and auditing across regulated industries.
Key Components of SecOps Automation
A mature SecOps automation strategy is anchored by an integrated technology stack that includes SIEM systems for centralized log aggregation and analytics, SOAR platforms for automated incident response workflows, and threat intelligence feeds that enrich alerts with actionable context.
Modern research highlights how these tools, when combined with endpoint security solutions (EDR), vulnerability scanners, and cloud security platforms, create a scalable, automated security ecosystem that enhances real-time detection, reduces false positives, and accelerates remediation across environments.
Common Use Cases of SecOps Automation
SecOps automation is most effective when applied to high-volume, repeatable security tasks that slow down SOC teams when handled manually. By automating detection, analysis, and response workflows, organizations can reduce alert fatigue and improve consistency across security operations. Below are some of the most common and impactful use cases of SecOps automation.
Automated Alert Triage
Automatically analyzes incoming alerts, filters false positives, and prioritizes incidents based on risk, severity, and context, allowing analysts to focus on real threats.
Phishing Detection and Response
Automates email analysis, URL and attachment scanning, and response actions such as blocking senders, removing malicious emails, and resetting compromised credentials.
Malware Containment
Detects malicious activity and immediately isolates infected endpoints using EDR tools to prevent lateral movement across the network.
Vulnerability Prioritization and Management
Automates vulnerability scanning and prioritizes remediation based on exploitability, asset criticality, and real-world threat intelligence.
User Access and Behavior Monitoring
Continuously monitors user activity to detect anomalies and enforce Zero Trust policies by automatically revoking or limiting access when risks are detected.
Cloud Misconfiguration Remediation
Identifies insecure cloud configurations and automatically applies corrective actions to reduce exposure in dynamic cloud and hybrid environments.
Compliance and Continuous Monitoring
Automates policy enforcement, audit logging, and compliance checks to maintain regulatory readiness and simplify reporting.
SecOps Automation vs Manual Security Operations
As cyber threats grow in volume and complexity, the gap between automated and manual security operations becomes increasingly clear.
| SecOps Automation | Manual Security Operations | |
| Speed & Efficiency | Responds in seconds using automated detection, triage, and response workflows, significantly reducing MTTR. | Response times depend on analyst availability, often resulting in delayed investigation and containment. |
| Accuracy & Consistency | Uses predefined rules, correlation logic, and playbooks to ensure consistent and repeatable responses. | Decisions vary by analyst experience, increasing inconsistency across incidents. |
| Scalability | Easily scales to handle thousands of alerts across cloud, hybrid, and on-prem environments without added staff. | Scaling requires hiring and training more analysts, which is costly and slow. |
| Risk of Human Error | Minimizes errors by automating repetitive tasks and enforcing standardized response actions. | High risk of mistakes due to alert fatigue, manual data handling, and time pressure. |
| Alert Management | Automatically filters false positives and prioritizes high-risk incidents. | Analysts must manually review alerts, leading to overload and missed threats. |
| Operational Cost | Reduces long-term costs by improving analyst productivity and reducing breach impact. | Higher operational costs due to inefficiency, overtime, and slower incident resolution. |
Benefits of SecOps Automation
SecOps automation delivers measurable advantages across speed, efficiency, cost, visibility, security posture, and compliance readiness, benefits repeatedly confirmed by industry research and SOC practitioner feedback.
Reduced Response Time
Automated workflows significantly shorten both Mean Time to Detect (MTTD) and Mean Time to Respond (MTTR) by executing threat correlation and response actions in real time rather than waiting for analysts to intervene manually. Organizations leveraging automation have reported up to a 33% reduction in MTTD and MTTR, helping contain threats before they escalate and reduce breach impact.
Improved SOC Efficiency
AI and automation reduce repetitive triage work and alert overload, allowing analysts to devote more time to strategic tasks like threat hunting. Research shows that automation can eliminate vast quantities of noise from daily workflows, enabling teams to focus on high-risk alerts and proactive defense.
Industry data also reveals that up to 60% of alerts go uninvestigated in manual environments, a problem automation helps mitigate by enriching and prioritizing alerts automatically.
Lower Operational Costs
Automation reduces the need for extensive manual intervention and overtime, lowering operational costs and reliance on manual labor. Automated tools often process security events much faster and more consistently than human teams, which can result in significant long-term savings compared with traditional SOC staffing.
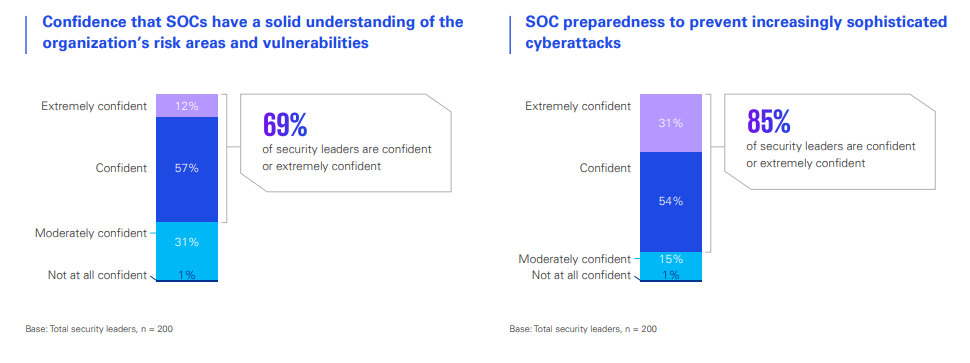
Better Visibility Across Security Infrastructure
By integrating data from endpoints, networks, cloud workloads, and identity systems into centralized workflows, automation platforms improve situational awareness and make it easier to detect anomalous activity across the entire environment. Unified security views have been shown to significantly cut down on blind spots and shed light on previously unnoticed threats.
Enhanced Security Posture
Automated security operations help organizations maintain consistent enforcement of controls and strengthen defenses against emerging threats. Studies show that automation reduces false positives and improves detection accuracy, empowering SOC teams to be more proactive and resilient.
Academic research also indicates that automated triage systems can reduce the volume of alerts analysts must manually review by more than 60%, freeing up critical resources for deeper investigation.
Improved Compliance Readiness
Automated workflows streamline audit trails, enforce policy checks, and maintain up-to-date compliance reporting. Teams using advanced automation and orchestration solutions often experience faster audit preparation times and more accurate compliance reporting than teams relying on manual processes.
Challenges and Limitations of SecOps Automation
While SecOps automation delivers clear benefits, implementing it is not without challenges. Many organizations face integration complexity, as connecting SIEM, SOAR, EDR, and cloud security platforms into a unified workflow often requires significant planning, custom APIs, and ongoing maintenance.
False positives and tuning issues can also emerge, especially when automation rules are applied too broadly, forcing analysts to intervene and fine-tune the system, ironically creating some of the same alert fatigue automation was meant to reduce.
Security experts warn about over-automation risks, where blindly automated actions might disrupt business operations or block legitimate activity. Additionally, skill gaps in security teams remain a key hurdle; staff must be trained to design, monitor, and maintain automation playbooks effectively.
Finally, the initial implementation costs for tools, integration, and training can be substantial, which can be a barrier for smaller teams or organizations with limited budgets.
Best Practices for Implementing SecOps Automation
Implementing SecOps automation successfully requires a thoughtful, phased approach.
- Start with high-impact, low-risk workflows – Focus on automating processes that deliver quick wins while minimizing operational risk.
- Maintain human oversight – Ensure analysts can review critical alerts and intervene when necessary to prevent over-automation errors.
- Use standardized playbooks – Create consistent, repeatable response procedures for faster, more reliable incident handling.
- Regularly test and optimize automation – Continuously refine workflows to adapt to new threats and reduce false positives.
- Align with business risk priorities – Focus automation efforts on protecting critical assets and high-risk processes.
- Integrate with existing security stack – Combine SIEM, SOAR, EDR, and cloud security platforms to ensure seamless, end-to-end automation.
SecOps Automation and the Future of Cybersecurity
The future of SecOps automation is being shaped by AI, machine learning, and increasingly autonomous systems. AI and ML are improving threat detection and response by analyzing vast amounts of data in real time, identifying patterns humans might miss, and predicting attack paths. This enables predictive threat response, allowing organizations to proactively neutralize threats before they materialize.
The concept of autonomous SOCs is gaining attention, where security operations are largely self-managing, with minimal human intervention needed for routine alerts. This doesn’t replace analysts but frees them to focus on high-priority investigations and strategic planning. Zero Trust architectures are also integrating tightly with automation, ensuring that policies, access controls, and anomaly detection are consistently enforced without manual oversight.
Cloud-native security automation is another emerging trend, allowing organizations to secure dynamic, distributed workloads efficiently. Automation platforms can automatically detect misconfigurations, enforce compliance policies, and respond to incidents across hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
Industry reports highlight that combining AI-driven automation with cloud-native and Zero Trust strategies significantly reduces breach impact and operational strain, while positioning enterprises to proactively defend against increasingly sophisticated threats.
SecOps Automation Tools and Platforms
When building a robust SecOps automation strategy, understanding the differences between SIEM, SOAR, and fully integrated automation platforms is essential. SIEM tools focus on collecting and correlating logs to provide centralized visibility and alerting, while SOAR platforms automate incident response workflows and security actions.
| Feature / Capability | SIEM | SOAR | SecOps Automation Platform (SIEM + SOAR) |
| Primary Purpose | Collects, normalizes, and correlates logs for visibility | Automates response workflows and orchestrates security actions | Provides end-to-end automation of detection, response, and remediation across the SOC |
| Alert Handling | Generates alerts based on correlated events | Acts on SIEM alerts using automated playbooks | Prioritizes, enriches, and responds to alerts automatically with human oversight when needed |
| Automation Level | Limited to correlation and rule-based alerts | High – executes workflows and response playbooks | Comprehensive – integrates detection, response, remediation, reporting, and compliance tasks |
| Integration Capabilities | Connects with log sources, endpoints, and cloud services | Integrates with SIEM, EDR, threat intelligence, and ticketing systems | Supports full integration with SIEM, SOAR, EDR, cloud platforms, and business applications |
| Scalability | Scales with log volume but may require tuning | Scales workflow automation; depends on playbook design | Fully scalable across hybrid and cloud environments with automation handling large alert volumes |
| Compliance & Reporting | Provides centralized log storage and basic reporting | Limited – generates workflow-specific reports | Advanced – automated audit trails, policy enforcement, and compliance reporting |
While SIEM and SOAR have distinct roles, only a combined SecOps automation platform delivers fully integrated detection, response, and remediation at scale.
Who Should Use SecOps Automation?
Organizations across industries are facing growing cyber threats, high alert volumes, and increasingly complex IT environments. SecOps automation helps security teams respond faster, reduce errors, and scale operations efficiently. It is particularly valuable where speed, consistency, and compliance are critical. The following groups benefit most from implementing SecOps automation:
- Enterprises – Manage complex, multi-layered infrastructures and reduce response times across large networks.
- Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs) – Deliver consistent security services to multiple clients without overloading analysts.
- Cloud-first Organizations – Gain automated visibility and remediation for dynamic, distributed workloads.
- Remote Workforce Environments – Enforce policies and detect threats across distributed endpoints efficiently.
- Regulated Industries – Maintain compliance, generate audit-ready reports, and minimize human error in sensitive sectors.
Frequently Asked Questions
It automates threat detection, response, and security workflows.
No. SOAR is a technology, but SecOps automation is a strategy.
No. It augments analysts by removing repetitive work.
SecOps automation improves incident response by executing predefined playbooks instantly, removing the delays inherent in manual processes.
Yes, SecOps automation can be highly beneficial for small businesses, particularly those with cloud-based solutions.
Final Thoughts
SecOps automation is no longer optional. As cyber threats scale, automation delivers the speed, consistency, and resilience modern security operations require. By combining SIEM, SOAR, threat intelligence, and well-designed playbooks, organizations can build security operations that are faster, smarter, and future-ready.








