What is Session Hijacking?
Session hijacking Attack is when an attacker takes control of a user session after successfully stealing a session ID. Hackers can obtain session IDs by using brute force or reverse engineering, which can then be used to de-authenticate a legitimate user’s web session in progress.
Session Hijacking – Detailed Guide
What is a session?
A session is a series of interactions between two servers during the span of a single connection. Let’s say you log in to your PayPal account. Your session has started and will end once you log out.
These sessions are used by Applications to store parameters relevant to the user and accommodate users’ requests. The session lives until after the predefined period of inactivity.
What is a Session ID?
A session ID is an alphanumeric string attached to the HTTP header that helps the server identify a user’s active session. Session IDs are commonly stored in cookies. Thus, Session Hijacking is also known as Cookie Side-jacking or Cookie Hijacking, because it relies on the hacker’s knowledge of your session cookie.
The attacker can successfully perform session hijacking once they have stolen the victim’s session cookie, which reveals their session key (session ID). Once authenticated, the attacker can take over the session, fooling the server into thinking it is the legitimate user.
What Happens After a Successful Cookie Hijacking Attempt?
After a successful Session Hijacking attempt, the attacker can perform all the actions the victim is authorized to do during that session. So this varies depending on the nature of the user’s activity.
If they are logged into their online banking service, the attacker can use the session to transfer money and make purchases on webstores.
Attackers even use session hijacking for identity theft and stealing confidential company data, which can then be leveraged for ransom.
Many large organizations use SSOs (single sign-on systems). These can be Business Intelligence Tools under a single HTTP header. If the attacker is successful in taking over a session cookie, he/she can get access to multiple web applications with users authenticated in single sign-on systems.
Primary Techniques Used For Hijacking Sessions
Brute Force
Brute Force is simply a guessing game. The attacker will try to guess a user’s session key, which may take multiple attempts. Sessions IDs are generated randomly and are usually very long, which is why the unpredictable values make it nearly impossible to guess Session IDs.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
The attacker can obtain a session key using javascript. The best example of this are crafted links with malicious code which runs once the user clicks on it. This is known as Cross-Site Scripting.
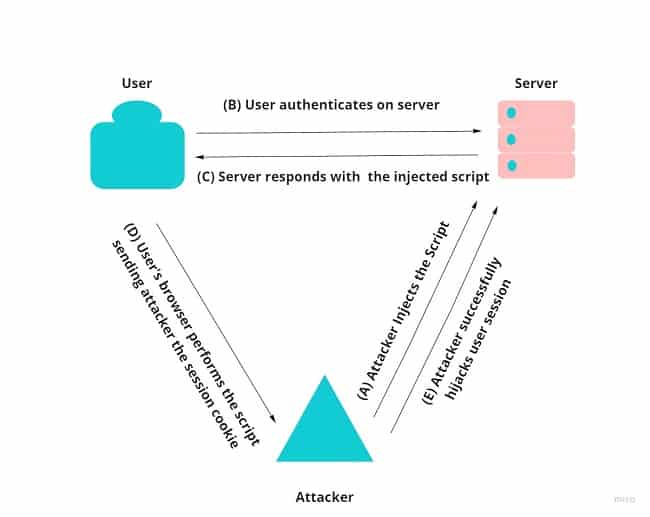
Packet Sniffing
Packet sniffing enables the attacker to monitor the victim’s network traffic. Once the user is authenticated on the server, the session cookie can be intercepted.
If a website has weak protocols in place, the sniffed session ID can be used to hijack the session by impersonating the original user on the targeted web application.
Session Spoofing
Session Hijacking exploits the user’s active session. In contrast, Session Spoofing exploits the user’s session ID to create a new session to impersonate the original user.
This way, the user will not be aware of the attack because, in session hijacking, the original user may sense something unusual if logged out of the session or the application crashes.
How To Prevent Session Hijacking?
The inherent flaws in the stateless HTTP Protocol make session hijacking a possibility. This is why taking specific security measures can help mitigate the risks associated with a successful session hijacking attempt.
Use Encryption:
A preferable solution would be to use HSTS (HTTP Strict Transport Security) to ensure encryption of all connections. Encryption will prevent the attacker from spoofing or obtaining any information. Alternatively, Packet headers can be encrypted using Internet Security Protocol (IPSEC) and other protocols like SSL & SSH. IPsec comes with two modes; transport and tunnel. It is recommended to use the Tunnel mode where the data is also encrypted along with the packet headers.
HttpOnly Attribute:
Use the “Set-Cookie” HTTP header to set the “HttpOnly Attribute.” This prevents access to cookies from client-side scripts. This method helps mitigate attacks involving javascript injection like Cross-Site Scripting (XSS). For additional security, you can also set attributes like “Secure” and “SameSite” to specific servers.
Identity Verification:
The server can put in place protocols other than the session key to identify the original user like the IP address the user usually logs in from and unusual patterns in the application usage. A typical example of this is a session timeout after a user has been inactive for a set amount of time.



