Table of Contents
If you are looking for excellent online protection and want to avoid surveillance, a VPN or Tor are two options worth considering. However, while they share some similarities, there are notable differences between them in terms of how they work and the benefits they provide.
In our Tor vs. VPN guide, we will take a closer look at both these tools so that you can decide which is best for you:
What is Tor?
Tor, also referred to as The Onion Router, is a decentralized network that offers anonymous communication. It operates through a distributed network of servers that are scattered worldwide and maintained by volunteers. Therefore, intercepting Tor connections is difficult as they do not rely on a single entity.
Here’s how Tor works:
- When you send a request, Tor encrypts it three times for three different relays – an entry relay, a middle relay, and an exit relay.
- Tor then sends the request to the entry relay, which removes one encryption layer and sends it to the next server. The entry relay can only see your IP address and not the encrypted message.
- The middle relay gets rid of the second encryption layer and sends the message with its final layer of encryption to the exit relay.
- The exit relay strips off the final layer of encryption and can read your decrypted message, but cannot tie it to the sender. This relay then forwards the message to the intended recipient.
When should I use Tor?
You should use Tor when you want to:
Browse the web anonymously
Tor connections are anonymous and close to impossible to trace back to their original users. You can securely visit websites without leaving any identifying information behind – be it on your device or on the website’s server.
Access the dark web
If you want to access the dark web, also known as darknet, then Tor is the easiest method to do it. Most dark web websites can only be accessed through a Tor connection and are not indexed by traditional search engines like Google.
Communicate untraceably
Tor can be used by individuals who want to stay anonymous – such as journalists, whistleblowers, activists, and crime victims – to communicate safely without the risk of being tracked or leaving any evidence trail behind.
Pros of Tor
Here are some pros of using Tor:
- Provides enhanced online anonymity through its complex encryption mechanism.
- The Tor software is free to use and download.
- Tor is difficult to intercept or shut down as the traffic goes through a network of nodes run by volunteers spread across the world.
Cons of Tor
Here are some cons of using Tor:
- Tor slows down your connection speed considerably as multiple encryption layers are added to your data.
- Exit relays might intercept and read message content.
- The Tor software is not available on many operating systems.
- Poor transparency or accountability in terms of the volunteers running the nodes.
What is a VPN?
A virtual private network (VPN) uses encryption to secure your data and sends it through a remote server. It offers various VPN protocols, plenty of servers in multiple locations, and features like a kill switch and split tunneling.
Since VPNs protect your internet traffic using 256-bit encryption, they can’t be intercepted by hackers and snoopers or brute-forced with current devices. These tools also allow you to mask your real IP address, enhancing your online privacy by a great deal.
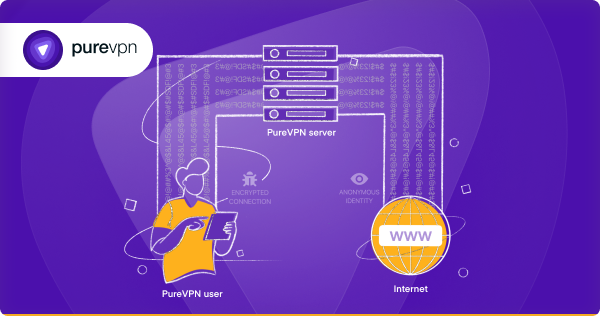
Here’s how a VPN works:
- The VPN application encrypts your traffic and routes it to a remote server that alters your IP address.
- Your data is decrypted by the VPN server, which forwards it to the intended destination.
- The data then arrives on your device from the network and undergoes the same encryption and decryption process.
As you can see, a VPN takes far fewer steps to protect your online privacy and security than Tor.
When should I use a VPN?

You should use a VPN when you want to:
Unblock geo-restricted content
Many streaming services like Hulu, Disney+ Hotstar, or BBC iPlayer block viewers from unsupported countries. With a VPN, you can switch your IP address to another country and gain access to otherwise unavailable content.
Use public Wi-Fi safely
If you are on the move and want to use a public Wi-Fi network, using a VPN is recommended. It will encrypt your entire connection to stop hackers from launching man-in-the-middle attacks or snooping on your traffic.
Dodge government censorship
Much of the web is blocked by the government in countries like China, leaving citizens unable to access many useful websites and services. A VPN lets you access the internet censorship-free as if you were in a different country.
Bypass ISP throttling
Internet Services Providers (ISPs) often block certain types of traffic – like video streaming and P2P file sharing – to prioritize certain services or manage network congestion. Using a VPN enables you to hide your traffic, meaning they can’t throttle it.
Pros of a VPN
Here are some pros of using a VPN:
- VPNs are typically much faster than Tor.
- Changing your IP address to another country barely takes a few clicks.
- Excellent solution for those who wish to stream geo-restricted content.
- A VPN uses top-of-the-line encryption to protect your data.
- Some VPNs like PureVPN are known for keeping no logs whatsoever.
- Easy-to-use apps are available, which can easily be downloaded on your device.
- Access to must-have features like a kill switch, split tunneling, obfuscation, and more.
Cons of a VPN
Here are some cons of using a VPN:
- A premium VPN will cost you money.
- Some VPN providers collect activity and connection logs.
- Slows down your connection to some extent but there are ways to increase your VPN speeds.
Note : Or try PureVPN 7-day trial for 0.99$.
The main differences between Tor and a VPN

Here are some key differences between Tor and VPNs:
Architecture
The main difference between Tor and VPN is their architecture. Tor is a free, open-source software that routes your traffic through a series of volunteer-operated nodes, making it difficult to trace your online activity.
A VPN is a service provided by a company that has a network of servers in different locations, and it encrypts your traffic and sends it to one of its remote servers, which then forwards it to the final destination.
Speed
Tor is known to be much slower than VPNs because it routes your traffic through multiple nodes, which adds to the latency. A VPN, meanwhile, can provide faster speeds as it only encrypts and decrypts your data twice.
Purpose
Tor is primarily designed for anonymous communication and browsing, whereas a VPN is designed to encrypt your traffic and protect your online activity from prying eyes. It is also commonly used to dodge internet censorship and access geo-restricted content.
Frequently asked questions
Can I use a VPN and Tor together?
Yes. It is possible to use VPN and Tor simultaneously. When you use both together, it is known as VPN over Tor or Tor over VPN based on which service you connect to first.
In Tor over VPN, you first connect to your VPN service and then use the Tor browser to access the internet. This results in your traffic getting encrypted twice, first with the VPN and then with Tor. It also hides the fact that you are using Tor – all your ISP would be able to see is that you are connected to a VPN.
In VPN over Tor, you first connect to the Tor browser and then connect to your VPN service. This results in an additional layer of privacy, as your VPN service won’t be able to see your original IP address and only the IP address of Tor’s exit node.
Is a VPN better than Tor?
It depends on what your needs are. If you want to browse and communicate anonymously, Tor is the right fit for you. If gaining better online privacy or access to geo-restricted content is important to you, a VPN is the better fit. However, we recommend using a VPN as it has better transparency, way more features, robust encryption, and faster speeds.