How to Run a Traceroute on Windows, macOS or Linux
Traceroute is a network diagnostic tool that maps the path data takes from one device to another across a network. By sending a small IP packet and tracking its route, traceroute helps identify slow or unresponsive nodes, pinpointing potential network inefficiencies or problems. Available in most operating systems, this tool is called ‘tracert’ in Windows environments.
How Does Traceroute Actually Work?
Traceroute dispatches an Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) packet to a designated target on the network. As the packet traverses the network, it “hops” through various routers and switches, each propelling it closer to its destination.
Throughout this process, traceroute records each hop, detailing the time taken for transmission and logging the names and IP addresses of the devices the packet encounters, from the initial router to the final target host.
What Does Traceroute Tell You?
Traceroute is valuable for pinpointing locations in a network where problems may arise, helping in network troubleshooting. For instance, if your office network is slow, traceroute can help identify exactly where the delay occurs.
By running traceroute, you see each step of the data’s journey across the network. If it shows that a particular router is processing data slower than expected, you can then address this specific point—perhaps by fixing or replacing the router—knowing the rest of the network is functioning correctly.
How Do I Run a Traceroute?
Here is how you can run a traceroute on different platforms:
How to Run Traceroute on Windows
- Press Windows key + R.
- Type cmd and hit the Enter button.
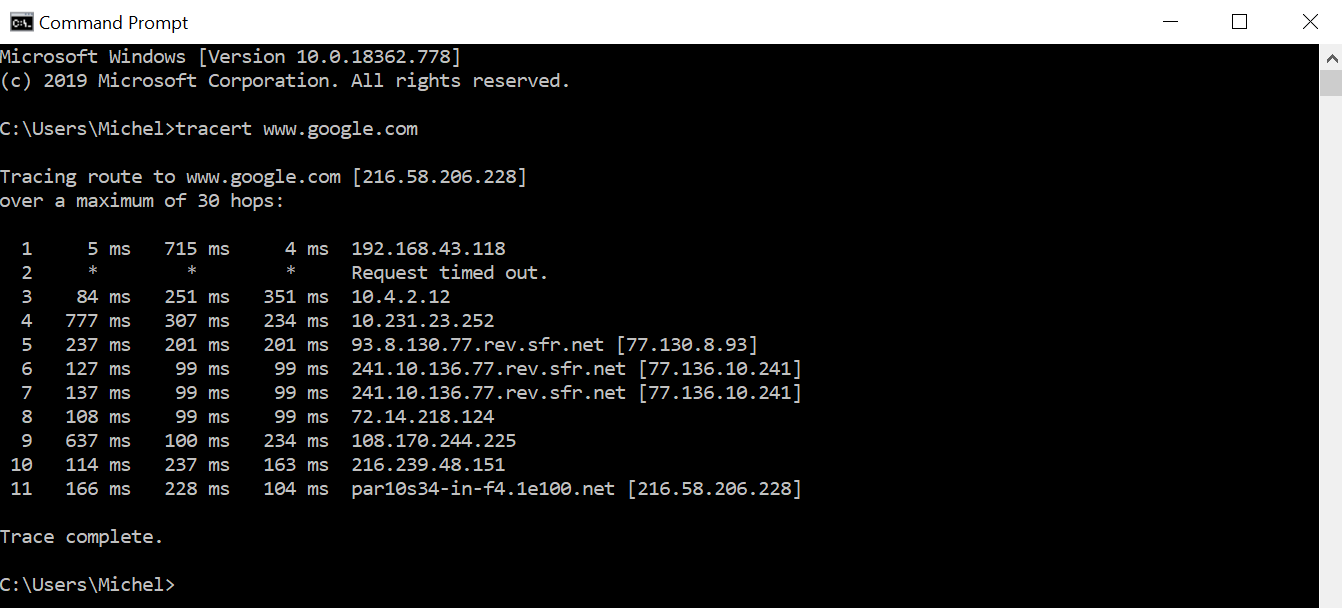
- In Command Prompt, type tracert [destination] and press Enter.
- The traceroute will run and the results will be displayed.
How to Run Traceroute on a macOS
- Go to Applications, then Utilities, and open Terminal.
- Type traceroute, and press Enter.
On older macOS versions, use the Network Utility tool found in the same Utilities folder to perform traceroute.
How to Run Traceroute on Linux
- Enter sudo apt-get install traceroute in the Linux terminal.
- Once traceroute is installed, open the terminal.
- Type traceroute [destination], and hit Enter.
Note: Replace [destination] with the IP address or domain you wish to trace.
How to Read a Traceroute
Learn how to interpret key metrics such as hop number, IP addresses, and round-trip times in traceroute results:
Hop Number
This indicates the step in the path from your device to the destination server. Each hop represents a router or gateway the packet encounters along its route.
IP Address
Each hop will typically display the IP address of the router it reached. Sometimes, instead of a raw IP address, you might see a domain name, which can provide clues about the router’s location or the network provider.
Round Trip Times (RTTs)
These values show how long it took for a packet to go from your computer to the hop and back again. Three times are usually shown for each hop to give an average and check consistency:
- Consistent times indicate a stable connection to that hop.
- Wide variations can suggest congestion or other types of network instability at or beyond that point.
Asterisks (*)
If you see an asterisk in place of a time value, it means the traceroute request timed out for that hop. This could be because the hop is configured not to respond, or there might be a network issue preventing a response.